Stabilizer bushings. Signs of malfunction. Consequences.
For the best damping of vibration and force impacts on the car body, the vast majority of suspension elements are connected by means of elastic elements.
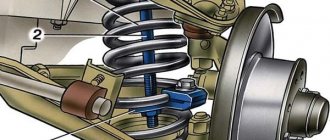
The same applies to the stabilizer. To secure it, special bushings (rubber bands, cushions) made of durable rubber or polyurethane are used. Over time, as the vehicle is used, these bushings may begin to deteriorate and noticeably lose their elasticity. The result of this is unsatisfactory operation of the stabilizer =. More serious defects may begin to appear, which will only grow faster over time. The first symptom indicating replacement of the bushings will be a slight knocking sound from the suspension. A similar knock can be observed with “tired” shock absorbers. Only in the case of bushings it will be heard not only on potholes and potholes, but also when entering relatively sharp turns. At the same time, the car often feels excessively rolly and sluggish. The knocking sound that appears will be a consequence of play that has arisen in the connecting nodes of the stabilizer arms due to worn bushings.
If measures are not taken in time, the knocking will only intensify in the future and will begin to accompany the operation of the suspension everywhere due to increasing deformation and destruction of the bushings. Body roll and excessive play in the steering wheel may occur. The car may “yaw” not only when turning, but also when braking or changing lanes. Most car manufacturers recommend changing stabilizer bushings every 30–40 thousand mileage. However, in our conditions it is better to focus on bushing wear. Therefore, a sudden knocking sound and slight rattling in corners will be clear signs of an impending component replacement.
As a popular method of checking the bushings for serviceability, it is proposed to drive the speed bump diagonally in 2nd gear. A dull knock appeared in the area of the pedals - most likely due to the hub bushings. You can also just crawl under the car and inspect everything yourself. A worn bushing will be pleased with the presence of cracks and abrasions characteristic of worn and cracked rubber. Auto mechanics sometimes also call these cracks “daisies.”
Also, the rubber of the bushings can simply harden and lose the necessary elasticity. If you can’t get a good look at the stabilizer bushings, just swing your hand strongly up and down and to the sides on the stabilizer itself. If you feel play, creaks and knocks in the lower part of the suspension, it means that the bushings have become unusable.
But for the best results, it is, of course, better to drive onto an overpass, an inspection hole, or use a lift. The only tools you will need are a crowbar or a mounting spade, which you simply need to rest against the bottom of the car and slightly “shake” the stabilizer where it connects to the body. If you feel noticeable play or loss of elasticity, then it’s time to think about replacing the bushings.
When is the transverse stabilizer bushing replaced?
Problems in this unit are detected during routine diagnostics. Usually, every 30 thousand mileage, rubber elements need to be changed, as they deteriorate - crack, tear or deform. Experienced motorists recommend replacing the set immediately rather than replacing each bushing individually, despite the fact that they may still be usable in appearance.