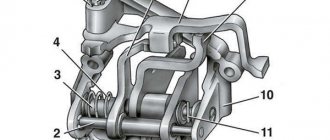
Repair of the front caliper VAZ 2110
The caliper in a car is one of the most important parts.
It is a unit necessary for attaching the brake pads of a vehicle. Only a small proportion of drivers pay due attention to the braking system, although this part of the car should be a priority. Many owners of domestic VAZ cars have managed to appreciate the importance of the caliper, or rather, the need for its full serviceability. For example, some drivers almost crashed into the vehicle in front because the braking system failed at the most inopportune moment.
The driver should definitely periodically check the serviceability of the brake caliper on the VAZ 2110 and other domestic car models. If this part is damaged, it can be restored. In cases where the possibility of restoring the caliper is excluded, the component part is completely replaced.
Replacement
VAZ 2109 rear brake cylinder
To replace the cylinder, you must have not only all the standard tools, but also a special wrench for unscrewing the pads. Replacement is carried out as follows:
- Raise the car on a jack and remove the wheel.
Note: It is advisable to install an additional stop, as the jack may not support it. In any case, it will be safer.
- You need to remove the brake drum. To do this, unscrew all the nuts that hold it in place.
- Use a large flat head screwdriver to remove the brake pads. To make it easier to remove them, you need to press on them from above, then quickly lower them down.
- It is necessary to unscrew the brake pipe from the cylinder. To do this, you will need the aforementioned key to unscrew the pads. It is needed in order to break off the tightened fitting. After this, you can use a regular key.
Note: it is important that the fitting does not rotate, otherwise the tube may be torn off along with it.
- After the tube is unscrewed, it must be plugged with a protective cap to prevent brake fluid from leaking out.
- Now you can remove the brake cylinder itself. It can be easily removed: you just need to unscrew it using a 10mm key.
- After this, you need to install the new cylinder back and screw on the brake pipes.
- Do the same thing, but in reverse order.
Replacing caliper guide pins and their boots on VAZ 2114-2115
The first step is to jack up the front of the car. Then remove the wheel and use a flat-blade screwdriver to bend the locking washers of the caliper bolts.
Then unscrew the two fastening bolts at the top and bottom, as shown in the photo.
Next, compress the brake cylinder using a screwdriver by inserting it between the bracket and one of the pads.
Next, you can lift the cylinder with the bracket up, as shown below, and move it to the side so that it is out of the way.
And now you can easily remove the caliper pins, both from above and from below, with minimal effort.
Then we clean the fingers from the old grease with a special product or buy a new one. Also, it is necessary to install a new boot if the old one is damaged.
Apply special caliper grease to the pin and under the boot, as shown in the photo. Then we put the finger in its place all the way so that the boot is securely fixed.
Now you can assemble the entire structure in reverse order, and do not forget to press the brake pedal several times before leaving the repair site so that the pads take their position in the guide.
Replacing caliper guide pins
If you begin to notice rattling of the calipers on your own car, then you should first pay attention to two things:
- On brake pad springs that may have weakened
- The caliper guide pins may have worn out due to lack of lubrication.
This article will examine the second option, when specific wear on the guide pins leads to similar dilemmas. First, you should pay attention to the condition of the anthers. If they are torn or even cracked, then they need to be replaced with new ones, and the fingers themselves must be re-lubricated. But more on this below.
Necessary tool for inspecting calipers on VAZ 2110, 2111 and 2112
- Flat blade screwdriver
- 13 and 17 mm wrench
- Copper grease
- Lubricant for caliper guide pins
- Brake Cleaner
Why does the brake pedal fail after bleeding?
Often, after servicing the system, for example, replacing brake fluid, pads, discs, drums, the brake pedal fails. What is the reason for such changes?
Failures may occur for some time after replacing pads, discs or fluid and bleeding the system. Be prepared that the pedal will begin to fall, and do not immediately try to operate the car in the previous mode. Give the new brake discs and pads time to get used to it - until this happens, the car will jerk when you press the pedal, which may even vibrate, which will be transmitted to the steering wheel. The general grinding-in of new pads and discs requires 250–400 km. If the symptoms persist after this, it is recommended to check the quality of the installation, as well as the elements themselves.
Often the reason why the brake pedal fails is a damaged or misaligned brake caliper. Its vertical axis shifts relative to the axis of the brake disc, so the system is unable to function normally. Or a working caliper may be poorly secured, which is why the brake pads will definitely not be able to properly rub into the disc.
Due to problems with the caliper, the new pad cannot press against the disc with the entire area of the anti-friction lining, so the latter wear out quickly, and the performance of the brakes cannot satisfy the car owner. In this case, when pressed, the pedal slowly goes lower and lower. That is why, when replacing pads, it is important to monitor the condition of the caliper, its axial relationship to the disc. This is a mandatory rule when changing only the pads, pads and discs, or these elements and the caliper at the same time.
Do-it-yourself dismantling of the caliper on a VAZ-2110
The very simple design of the product and the triviality of the process of dismantling it allow even a novice motorist to carry out repairs and maintenance. If you carefully follow the recommendations below, you are unlikely to encounter difficulties at any stage of the process. You will save a lot of money spent on a trip to a service station, and a considerable amount of time, because the service time is comparable to the time required to travel to the workshop.
Dismantling VAZ caliper
The sequence for dismantling the product is as follows:
- The first step is to jack up the car and remove the wheel. To be on the safe side, it can then be placed under the bottom of the car in case the jack fails;
- On a VAZ 2112, the caliper is attached to the bracket using two M17 bolts, which you should unscrew. Penetrating lubricant may be needed to strip the bolts;
- If you need to replace the VAZ caliper or carry out a comprehensive repair, unscrew the product from the brake hose. You seal the hose tip and you can begin further disassembling the product.
Repair
Replacing the front brake cylinder of a VAZ 2109
In some cases, the front cylinder fails. Therefore, the right decision would be to replace it. However, you can do it differently. If you want to save money, you can try to repair it yourself.
Note: The front cylinder is usually inexpensive, so you won't save much money.
If you still want to carry out repairs, you need to do the following:
- Raise the car on a jack.
- Remove the wheel. It cannot be removed unless all the nuts are unscrewed. There are few of them and they are very easy to remove. The 19 key will help in this matter.
Note: to make it safer to work with the car in the future, you can make an additional support. A stump or other object the height of a wheel is suitable for this. It is desirable that this item be stable. After this, the car can be completely lowered from the jack.
- Then you need to remove the brake disc. You must act very carefully so as not to harm him. It is better to remove it with a crowbar. Pull the disc toward you with slow movements. At the same time, you need to try not to pull it out.
Replacing the front brake cylinder of a VAZ 2109
- Unscrew all nuts holding the drum.
- Remove the brake cylinder.
- Its repair consists of replacing the cuff and boot. They must be thoroughly lubricated with brake fluid and then installed in place.
Note: The cylinder should also be lubricated to prevent it from rusting. However, later it will be more difficult to install it in place, as it will slide.
- Return the cylinder to its place.
Note: To install it easily, you need to press it lightly.
- It is tightened with a 10mm wrench. After this, you should take a flat-head screwdriver and place the cylinder straight.
- Repeat all steps in reverse order.
Lubricating calipers: how, with what and why?
Any “extra” sound coming from the front suspension will certainly alert an experienced motorist. A worn-out bearing, a loose ball or a spinning wheel can lead to loss of controllability and even cause an accident. However, of the many knocks that chassis parts can make, the one that stands out the most is the sound made by the brake calipers - or rather, their brackets and guides. Today we will fight him.
This unpleasant and loud defect is known firsthand to many drivers, and it causes completely different reactions. Most often, the owner prefers “not to interfere with the car’s operation” - after all, this is the easiest way, and the “sound accompaniment” does not particularly affect the operation of the braking system itself. However, there are many meticulous motorists who fight sound in various ways - for example, by lubricating the guides and even modifying them.
The knocking noise occurs due to excessive clearance in the guide-bracket pair.
What to lubricate
It would seem that what could be simpler than lubricating the caliper guides? Many owners do this - during the next “overhaul” of the brake system, they take and lubricate their fingers with whatever comes to hand. As a rule, the garage assortment includes lithol and its derivatives, as well as graphite. More advanced people are puzzled by finding a specialized composition intended specifically for use in brake system components.
And now - surprise: in most cases, both of them do the wrong thing! Yes, the caliper guide pins do need to be lubricated, but not with what is usually considered a suitable lubricant, even if it is positioned as such in a car shop.
Car manufacturers produce guide lubricants under their own brands.
Here is a list of original OEM lubricants from some automakers, indicating catalog numbers:
- BMW 81 22 9 407 103, 83 23 0 305 690;
- FORD/Motorcraft D7AZ-19A331-A, XG-3-A;
- Volkswagen/Audi G 052 150 A2;
- LAND ROVER RTC7603, SYL500010;
- HONDA 08C30-B0224M, 08798-9027;
- MAZDA 0000-77-XG3A;
- NISSAN 999MP-AB002;
- SUZUKI 99000-25100;
- TOYOTA 08887-80609;
- CHRYSLER/Mopar J8993704;
- Volvo 1161325-4.
There are also lubricants produced by companies producing auto components and chemicals under their own brands:
- ACDelco 89021537 (10-4022);
- Federal Mogul F132005;
- FTE Automotive W0109;
- Stahlgruber 223 1712, 223 1729;
- TRW Automotive PFG110.
Such different lubricants
Unfortunately, in the vast majority of cases, car dealerships (both online and offline) will usually offer “the wrong thing” - that is, anti-creaking lubricant, which simply cannot be used in guides!
The fact is that copper and ceramic anti-squeak pastes are intended for application to the back side of the pads and mating elements of brake calipers, but they are not suitable for “guides” for several reasons. Firstly, after lubrication with grease, lithol, “graphite” and other lubricants based on mineral oils, the rubber boots on the fingers almost always swell, stop sticking to the fingers and, in fact, simply stop performing their function.
Secondly, only special greases based on synthetic oils and a thickener are suitable for lubricating the guides. Thanks to this, the lubricant becomes refractory and does not “drain” from the guides after heating, and also does not coke over time from exposure to water and high temperatures. High-quality specialized lubricants can easily hold up to +300C, but at the same time they are non-aggressive to seals. Moreover, such lubricants not only do not melt, but also do not dissolve in water, alkalis, dilute acids, brake fluid, as well as methanol and ethanol.
Using the wrong lubricant in practice can lead to the opposite effect - that is, the lubricated guide pins become sour in the caliper, which is why the floating bracket loses its mobility, and the pads begin to jam and overheat.
On thematic forums, hundreds of pages are devoted to choosing the “right” lubricant for guides, but the theoretical calculations and practical reviews given often contradict each other, which leads to even greater confusion.
We are developing a jammed piston of the front brake mechanism of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099
The brake mechanisms (calipers) of the front wheels of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 vehicles operate under constant exposure to an external aggressive environment (salt, dirt, water, etc.). In this regard, it is recommended to inspect and service calipers and brake pads every 15 thousand km. Jamming or “souring” of the pistons in the caliper cylinders is most often the result of a lack of periodic monitoring of the condition of the brake mechanisms, damage to their protective boots, severe wear of the brake pads in which the pistons extend too far from the cylinders, thereby coming under external influence, the presence of water or foreign substances. impurities in brake fluid.
Reference: the pistons of the brake mechanisms of the front wheels of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars have a mirror coating, the same coating is found inside the cylinders. The cylinders are equipped with rubber rings that return the pistons to their original state after extension. On the outside, the pistons are protected by anthers (protective caps with retaining rings).
Damage to the mirror coating of the pistons (“souring”) leads to a loss of their mobility in the cylinders and, as a consequence, to incomplete release of the front wheels, since the pads are constantly pressed against the brake discs. In this case, accelerated wear of the pads, overheating and warping of the brake discs occurs, fuel consumption increases, the vehicle's controllability (pulls to the side) and its dynamics are impaired, vibration and beating appear when the brake pedal is pressed.
There are at least two ways to develop a soured piston:
— without removing the brake mechanism from the car;
- with the brake mechanism removed.
In the first case, it is necessary to jack up the car, remove the wheel, clean the outside of the caliper from dirt, disconnect and lift its floating bracket.
Raise the floating caliper bracket and clean the brake cylinder
We remove the retaining ring and the cylinder boot, remove dirt from under it using a rag soaked in gasoline and a hard brush or toothbrush. Lightly press the brake pedal so that the piston moves out a little (a centimeter at most) from the cylinder. We clean it again, being careful not to damage the piston mirror and remove only dirt and deposits. You cannot clean the piston with sandpaper, as this can damage the mirror. A popular way to clean deposits is to use a rough wooden block, which will remove deposits and not damage the cylinder. Remove the cap from the brake fluid reservoir and, using an adjustable wrench or vice, push the piston back into the cylinder. We press the brake pedal, pushing out the piston, and press it down again. We carry out this procedure for developing his mobility 20-30 times. Then we apply graphite lubricant to the protruding part of the piston, install a new boot and retaining ring.
The advantage of this method is that there is no need to drain the brake fluid from the car’s brake system circuits and pump the brakes.
In the second case, we remove the brake cylinder and disassemble and develop it. This method is suitable for a major overhaul of calipers, since it is necessary to either drain the brake fluid or plug the brake pipe, which still risks losing a certain amount of fluid and requires bleeding the brakes after the work is completed.
The piston must be squeezed out of the cylinder either before removing it (by pressing the brake pedal), or with the piston already removed, pressurized air must be supplied into the hole under the brake pipe. Before extruding, remove the retaining ring and boot from the piston. We try not to scratch the removed piston. We clean it from dirt and oxidation using the method described above, if necessary, change the rubber sealing ring, rinse and blow through the cylinder. Before assembly, lubricate the inside of the brake cylinder with brake fluid, and lubricate the piston itself with graphite lubricant. We press it inside the cylinder (for example, using a vice), put a new boot and retaining ring on top.
All of the above manipulations make sense only if there is minor damage to the piston or cylinder. If the piston is completely jammed and it is impossible to develop it, the brake cylinder with the piston should be replaced.
Notes and additions
— After developing the pistons of the brake cylinders of the front wheels of the car, it is necessary to lubricate the guide pins.
Twokarburators VK - More information on the topic in our VKontakte group, on Facebook Twokarburators FB and on Odnoklassniki - Twokarburators OK
More articles on the braking system of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
— Checking and adjusting the free play of the brake pedal of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
— Checking the brake system of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
— Diagram of the parking brake system of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
— Diagram of the working brake system of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
— Replacement of front brake pads on VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
— Replacement of rear brake pads on VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
Front brake pad guide bracket VAZ 2112 R14 (1 piece)
- We guarantee fast processing of your order during business hours (we work from 11-00 to 20-00, Saturday and Sunday are days off).
- We guarantee reliable packaging of your order (when sending it by Russian Post or transport company).
- We guarantee the fastest possible dispatch of your paid order (within 2-4 business days after receipt of payment).
- We guarantee a refund or exchange for another product (with recalculation) within 14 days from the date of receipt of the order (the product must be in good condition, without traces of installation, delivery costs are not reimbursed).
- We guarantee a free exchange of goods (transportation costs at our expense) if the purchased goods turn out to be defective.