Today we’ll talk about the crankcase on Kalina with an 8-valve engine. And to be more precise, about cleaning this system. Crankcase gases straight from the crankcase (hence the name) are sent mixed with air to the intake manifold for re-burning, thus saving a certain percentage of fuel. So, along with the gases, oil particles enter the system and clog it.
It is this oil that needs to be cleaned from the crankcase ventilation system. Over time, plaque forms on the walls of the hoses, which impedes the passage of gases.
In the Kalinovsky engine, in the valve cover, there is a special separator that separates crankcase gases from the oil. It gets clogged the most. So, let's get started. The entire ventilation system consists of 3 pipes. We need to unscrew them.
Then remove the valve cover. There are two bolts on the back side, unscrew them and get to the separator.
The easiest way to clean it from oil and deposits is in a bath of gasoline or solvent.
While the separator is acidifying, you can work on the pipes. In general, if they are heavily soiled, it is advisable to replace them with new ones. In my case, I replaced only one - coming from the valve cover to the air filter pipe. The rest were washed with carburetor cleaning fluid (great stuff, it corrodes absolutely everything). The separator itself can also be washed a second time with this thing.
We wipe everything with a clean cloth and put it back together as it was. Pay attention to the condition of the valve cover gasket. It is considered disposable and it is better to replace it with a new one each time you remove it in order to avoid oil leaks.
Modification of the crankcase ventilation system Kalina 8 valves
This system could be improved a little. One of the 3 pipes supplies crankcase gases directly to the throttle valve assembly next to the IAC. If they contain oil, it will definitely settle there. This is how the IAC becomes clogged. So, to avoid this, you can embed a regular fuel filter right in the middle of this pipe.
It will trap oil particles contained in crankcase gases. After a few hundred kilometers, you will see for yourself. Monitor the condition of this filter and promptly change it to a new one. On average, as practice shows, it needs to be changed every 1000 kilometers.
Video
Tools:
- Open-end wrench 10 mm
- Open-end wrench 13 mm
- Open-end wrench 17 mm
- Medium Phillips screwdriver
Parts and consumables:
- Gasoline/kerosene
- Rags
- Sealant
- Automotive compressor
- Cylinder head cover gasket (if replacement is needed) -2108-1003270-10
Read more: Replacing rear springs on a gazelle video
Notes:
The crankcase ventilation system of the VAZ Lada Kalina 1118 tends to accumulate tarry deposits from crankcase gases, which make it difficult to remove these gases into the engine cylinders for combustion. Because of this, the gas pressure inside the engine increases and oil leaks through the seals appear. We recommend cleaning the crankcase ventilation system before each oil change.
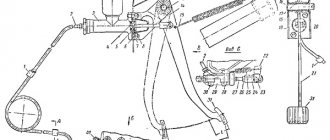
1. Remove the decorative plastic engine cover.
2. Loosen the clamp and disconnect the hose of the large branch of the crankcase ventilation system from the air supply pipe.
3. Disconnect the second end of the large crankcase ventilation system hose from the fitting on the cylinder head cover and remove the hose.
4. Similarly, remove the hose of the small branch of the crankcase ventilation system by disconnecting it from the fittings of the throttle assembly and the cylinder head cover.
5. Remove the supply hose of the crankcase ventilation system by disconnecting it from the fittings of the cylinder block and the cylinder head cover.
6. Rinse the hoses with gasoline or kerosene, blow with compressed air and dry. Clean the holes in the fittings and pipes for connecting the hoses.
7. Unscrew the two fastening nuts and remove the cylinder head cover.
8. Unscrew the long 1 and short 2 bolts securing the oil separator from the inside of the cylinder head cover and remove the washers.
9. Remove the oil separator housing.
10. Remove the mesh pack from the cylinder head cover.
11. Thoroughly rinse the screens, oil separator housing and cylinder head cover with kerosene.
12. Turn the meshes in the bag so that they are oriented in the same way, and install the bag in the lid so that on one side it rests against the protrusions in the lid, and on the other side you can see the hole for the bolt that secures the oil separator of the VAZ Lada Kalina 1118.
13. Install the oil separator housing and tighten its mounting bolts.
14. Check the condition of the cylinder head cover gasket and replace if necessary.
15. The hoses of the crankcase ventilation system and the cylinder head cover of the VAZ Lada Kalina 1118 are installed in the reverse order of removal.
The article is missing:
- Photo of the instrument
- Photos of parts and consumables
- High-quality photos of repairs
If, while operating a LADA car, you notice that during load (when the air conditioner is running, the heating is on, etc.) in a traffic jam, the engine begins to operate unstably (troits, pulls poorly, etc.), perhaps the reason lies in the ventilation system crankcase The article proposes to solve the problem by installing a PCV valve from a foreign car.
Purpose of the adsorber purge valve
In the Lada Kalina model, as in principle in any other car equipped with distributed fuel injection, an adsorbing system is necessary to localize the resulting gasoline vapors. They accumulate inside the tank after the engine stops, and after a certain time necessary for the transformation of these vapors into a condensation state, they turn back into liquid fuel. The remaining volume of vapor that failed to return to the tank moves to the adsorber, where it is retained by two valves. The first (gravity type) is necessary to prevent fuel spillage when the LADA Kalina body turns over (in an accident, etc.), and with the help of the 2nd, the pressure indicator inside the tank is monitored.
Breather oil: what to do and how to find the cause
Let's start with the fact that during engine operation, so-called crankcase gases accumulate in the crankcase. To prevent excess pressure from being created, there is a special valve for ventilation. This solution allows the closed crankcase to communicate with the atmosphere. This valve is the breather. In simple words, a breather on an internal combustion engine is actually needed to equalize the pressure inside the engine.
It should be noted that in the crankcase gases mix with oil mist. As a result, lubricant particles enter the breather. Although there is a special oil trap inside the device, a certain part of the oil may escape out. Given this information, minor contamination of the system is acceptable, which is normal. In cases where a lot of lubricant leaks, you should look separately for why oil is leaking from the breather.
On injection engines, traces of oil getting into the throttle area are noticeable, the power unit also loses its throttle response and power, and fuel consumption increases noticeably. It turns out that to check it is necessary not only to inspect the outer surfaces under the hood, but also to remove the air filter, throttle assembly, etc.
Changing the purge valve on Kalina
The replacement procedure itself is not a complex undertaking. To perform this, the owner will need to acquire a regular Phillips screwdriver and know where the valve is located.
Below we provide an algorithm of actions that allows you to quickly and efficiently complete this procedure.
- Disconnect the corresponding terminal from the negative terminal of the battery.
- You will need to disconnect the power connector from the valve itself.
- For ease of access to the unit, we move the suction pipe of the intake system slightly to the side together with the “Max Air Mass Airflow” sensor. For this purpose, use the indicated screwdriver to loosen the clamp of the pipe and perform the action.
- Now we proceed to dismantling the unit. To do this, disconnect a pair of fittings located on the sides of the product. One of the fastening elements is fixed with a latch and to dismantle it, you will need to recess the latch, then lift the antennae and finally tighten the fitting to the side.
- Before installing a new component, we check that the markings on both valves match and make sure that they are identical.
- Installation and fixation of the product is carried out in the reverse order.
The canister purge valve has been replaced.
Let's sum it up
The work of replacing the valve is simple, however, when the owner of a Lada Kalina is not confident in his capabilities or does not show the desire to carry out repair operations in such a high-risk unit as the fuel supply system, we recommend using the services of a specialized workshop.
EGR valve: what is it
The car's EGR Exhaust Gas Recirculation system is a very vague and rather capricious thing, especially with the very low quality of fuel that is found in our area, quite often. The ambiguity of this system lies in the fact that its purpose is purely environmental. waste recycling system
gases or USR, is designed to reduce the amount of nitrogen oxides in the car exhaust. What is the USR, why is it needed and how its malfunctions are expressed, we will talk about all this for now.
What is the EGR valve for?
We should start with the fact that the USR system is installed on most diesel engines and gasoline, naturally aspirated units. The essence of this system is that at certain moments the valve
EGR and a portion of
exhaust gases
.
Schematic representation of the operation of the USR system.
Thus, the amount of oxygen in the fuel mixture is reduced, which in turn reduces its combustion temperature. And at a lower combustion temperature, the amount of nitrogen oxides in car exhaust decreases quite significantly. If the engine is turbocharged, then the range of application of the USR is significantly narrowed, which makes its installation irrational. In such cases, other solutions are used to reduce the amount of harmful components of automobile exhaust.
Exhaust Gas Recirculation does not work at idle speed, it is not used when the engine is cold, and the EGR valve closes when the throttle valve is wide open.
Diagram of the standard crankcase ventilation system
The crankcase ventilation system of VAZ engines consists of two circuits that operate at different load modes and speeds:
- The small ventilation circuit is connected to the valve cover and the intake manifold (behind the throttle body). This connection diagram provides intensive crankcase ventilation due to the vacuum that occurs in the intake manifold when the throttle is closed. To avoid an effect such as hyperventilation, the cross-section of the small circuit is limited by a jet in the cable throttle body with a diameter of 1.7 millimeters. This circuit operates in the region of 800-1500 rpm.
- A large ventilation circuit is connected to the valve cover and the air pipe (in the pre-throttle space). This scheme provides intensive crankcase ventilation at high speeds. The cross section of the large contour is 16-18 millimeters
Read more: Kixx atf multi article number
Examples demonstrating the shortcomings of the standard crankcase ventilation system:
- A car is going down a hill with the gear in gear. In this mode, the engine operates at higher speeds with a reduced load. A high vacuum is created in the crankcase, and a large ventilation circuit is connected, in which there are no control valves. Since both circuits are connected to one volume of the oil trap, a strong vacuum in the crankcase will draw a fresh portion of air bypassing the throttle. The mass air flow sensor will show increased air flow, and the ECU will try to close the throttle. Having realized that this is not possible (it is already closed), the lean mixture will be corrected by increasing the fuel supply (fuel consumption will increase). As a result, the entire internal volume of the engine will work as a parallel receiver of very significant volume, connected to the intake, bypassing the throttle. It is this volume that will interfere with the formation of a high-quality mixture.
- A car in a traffic jam drives under tension with additional consumers (for example, the air conditioner is on). The compressor clutch is connected, the load increases abruptly. The engine does not have enough air, it begins to pull it from the crankcase, bypassing the throttle. But the ECU is also aware of the clutch engagement and also supplies more air by opening the throttle. The vacuum drops sharply, the vacuum brake booster (VBR) does not have enough strength to hold the car. Leap forward. The ECU sees an increase in oxygen and closes the throttle. A sharp increase in vacuum, VUT seizes. The car jerks, the transmission hits. And so on ad infinitum.
As a result, in both cases, when the engine is running, speed jumps occur and the engine choke under the load. Jerking and vibration are possible on manual transmissions, automatic transmissions and automatic transmissions. To eliminate these shortcomings, it is proposed to modify the design according to one of the presented schemes.
USR system management
recirculation system is controlled by the electronic engine control unit. And the command to open or close the EGR valve can be given based on:
- coolant temperature sensor;
- crankshaft sensor;
- throttle position sensor;
Read
In various car models, either all of the listed sensors are used to control the USR valve, or some of them, and in some cases, only the coolant temperature sensor.
What does the EGR valve look like on a Chevrolet Lacetti?
One way or another, the operation of the USR valve is always controlled by automotive electronics. And while this system functions normally, the driver practically does not feel its operation at all. The useful work of the USR system outside of environmental issues is very unnoticeable. This system allows you to save about three percent of fuel on gasoline engines. Also, in some cases, the USR system prevents fuel detonation in the engine. But this phenomenon in itself is rare and extraordinary. As for diesel units, if they have a properly functioning EGR system, they operate more smoothly, softly, and quietly. In addition, in diesel engines, the formation of soot is reduced through the USR. That's all the bonuses that the exhaust gas recirculation system provides the owner.
What is an EGR valve and what is an exhaust gas recirculation system for?
REAL TAXI DRIVER A huge flaw in the design.
EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation) System - Evil or Good?
In this video I explained in Russian why the EGR valve is needed
, but to jam it or not, draw your own conclusions.
Description of design
Engine cross section
: 1 — drain plug; 2 — engine sump; 3 - oil filter; 4 — coolant pump; 5 — catalytic collector; 6 — oxygen concentration sensor; 7 — inlet pipe; 8 — fuel injector; 9 — fuel rail; 10 - receiver; 11 — cylinder head cover; 12 — camshaft bearing cover; 13 - camshaft; 14 — lower crankcase ventilation hose; 15 — valve adjusting washer; 16 - crackers; 17 — pusher; 18 — valve springs; 19 — oil deflector cap; 20 — valve guide; 21 - valve; 22 — spark plug; 23 — cylinder head; 24 - piston; 25 — compression rings; 26 — oil scraper ring; 27 — piston pin; 28 — cylinder block; 29 — connecting rod; 30 - crankshaft; 31 — connecting rod cover; 32 — oil level indicator; 33 — oil receiver
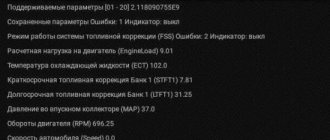
The VAZ-21114 engine is a gasoline, four-stroke, four-cylinder, in-line, eight-valve, with an overhead camshaft. The cylinder operating order is 1-3-4-2, counting from the crankshaft pulley. Power system - distributed fuel injection (emission standards Euro-2 or Euro-3). The engine with the gearbox and clutch form the power unit - a single unit mounted in the engine compartment on three elastic rubber-metal supports. The front right support is attached to the bracket on the cylinder block, and the front left and rear ones are attached to the brackets on the gearbox housing. The front right and left supports of the power unit, although externally similar, are not interchangeable. On the right (along the direction of the car) on the engine there are: a drive for the gas distribution mechanism and a coolant pump (by a toothed belt), a generator drive (by a serpentine belt), an oil pump, and a crankshaft position sensor. On the left are: thermostat, camshaft position sensor, coolant temperature sensor, coolant temperature indicator sensor, starter (on the clutch housing). Front: spark plugs and high voltage wires, ignition coil, knock sensor, oil level indicator, lower crankcase ventilation hose, generator. Rear: receiver with throttle assembly, fuel rail with injectors, intake pipe and catifold, oil filter, oil pressure sensor. The air filter housing with mass air flow sensor is mounted on brackets to the left of the engine. The cylinder block is cast from cast iron, the cylinders are bored directly into the block. The nominal diameter of the cylinder is 82.00 mm with a tolerance of +0.05 mm. The calculated gap between the piston and cylinder (for new parts) should be 0.025-0.045 mm. It is defined as the difference in size between the minimum cylinder diameter and the maximum piston diameter and is ensured by installing a piston of the same class as the cylinder into the cylinder. Depending on the dimensions (diameters) obtained during machining, the cylinders and pistons are divided into five classes. The class of each cylinder in accordance with its diameter is marked in Latin letters on the lower plane of the cylinder block: A - 82.00-82.01 B - 82.01 -82.02 C - 82.02-82.03 D - 82.03-82.04 E - 82.04-82.05 (mm). The maximum permissible cylinder wear is 0.15 mm per diameter. During repairs, the cylinder diameter can be increased by boring by 0.4 or 0.8 mm to accommodate pistons of increased diameter.
Engine (view from the right along the car)
: 1 — oil pan; 2 - oil filter; 3 — catalytic collector; 4 — right support bracket of the intake pipe; 5 — coolant pump pipe; 6 — inlet pipe; 7 - receiver; 8 — fuel rail with injectors; 9 — front cover of the gas distribution mechanism drive; 10 — lower crankcase ventilation hose; 11 - generator; 12 — generator drive belt; 13 — tension roller of the generator belt; 14 — bracket for the front right support of the power unit; 15 — generator drive pulley
EGR system malfunctions
Diagnosing problems with the described system is not as simple a task as it might seem at first glance. The trouble is that there are no pronounced symptoms characteristic of EGR problems. The engine seems to be running rough, it seems to be malfunctioning, but it doesn’t seem to be. And only a professional can suspect the exhaust gas recirculation of such unstable engine operation. But before that, various sensors, components and systems of the car are checked. Actually, what problems may arise here:
- deposits of soot and other elements on the parts of the EGR valve, leading to it jamming in any position;
- burnout of the EGR valve;
- clogging of the USR line itself;
- violation of electronic control systems for the USR valve;
If a valve or line is simply clogged, cleaning them, in general, is not difficult, although in some cases such cleaning is simply impossible. Well, if the valve burns out, then you will have to change it, and this, as already mentioned, is by no means cheap.
There are virtually no symptoms specific to problems with the EGR valve. This is, for example, unstable engine operation at idle speed, unmotivated dips in power, lack of pronounced acceleration when the throttle valve is fully opened, and other signs of disturbances in engine operation.
One way or another, do not rush to change the EGR valve or turn it off if there is no obvious damage to the valve and its parts. Perhaps the problem here is not entirely in the USR, because this system is closely interconnected with other components and systems for regulating air supply and exhaust gas removal.
Schemes for upgrading the crankcase ventilation system
Schemes for modifying the crankcase ventilation system, as well as a description, are provided by IgorRV.
For LADA cars with manual transmission and AMT (“robot”), scheme No. 1 “Crankcase ventilation scheme with PCV valve for E-GAS and cable throttle” is suitable:
It is necessary to install a PCV valve (article 94580183, price about 400 rubles) from a foreign car into the small crankcase ventilation circuit. When connecting the PCV valve to a small circuit on an E-GAS, use a new hose (petrol-oil-resistant 8 mm without fabric reinforcement). On a cable choke, connect to the receiver, not to the choke.
Read more: Oil for Priora sills
As a result, the valve will shut off the circuits in transient modes, which will allow:
- Accept the load without jerking or dropping engine speed (for example, when the compressor is running, heated windows, seats, etc.).
- Reduce vibration load at idle
- Increase traction from the bottom (noted by owners of automatic transmission with VAZ-21126 engine, manual transmission with VAZ-21227, 21126 and 11186 and AMT with VAZ-21127).
- Get a sharper response to the gas pedal and faster shifts (on AMT). Perhaps due to the fact that the valve does not allow the engine to slow down, maintaining a more optimal switching algorithm.
- Reduce oil consumption through ventilation.
The valve replacement period is 40,000 km.
For LADA cars with automatic transmission (Jatco) and AMT (“robot”), scheme No. 2 is suitable:
Description of scheme No. 2: The pressure reducing valve is connected in series to a large ventilation circle. Thus, it regulates the flow of crankcase gases at high speeds and during transient processes. This allows:
- Exercise full control over the flow of crankcase gases between the small and large circuits.
- Improve engine operating mode.
- Reduce vibration load.
- Reduce oil release into ventilation.
For LADA cars with automatic transmission (Jatco) and AMT (“robot”), scheme No. 3 is suitable:
Description of scheme No. 3: To improve the operation of the braking system and facilitate the process of holding the car on the brakes in mode “D”, an “Ejection Pump” was used. Due to the flow of crankcase gases from the small circuit, the vacuum in the tube leading to the vacuum booster increases. This happens at low speeds, which is very helpful when driving in traffic jams. Keeping your foot on the brake all the time is not very easy, but this pump makes the task easier.
- Getting rid of vibrations, failures, transmission shocks.
- The engine begins to operate more calmly and softly.
- The force on the brake pedal becomes less.
- The air conditioner turns on almost imperceptibly.
- ejection pump (article 10793 VIKA, price 546 rubles);
- pressure reducing valve (article 1117701500 JP GROUP, 422 rubles);
- PCV valve (article 94580183 GENERAL MOTORS, 400 rubles);
- clamps (about 10 pieces, 600 rubles);
- thin, petrol-resistant 8 mm hose 50 cm (100 rubles);
- standard ventilation pipe.
Installation example on video:
By the way, there are other ways to modify the crankcase ventilation system. Are you ready for such modernizations? Let us remind you that modification of the ignition system (installation of capacitor ignition coils in the harness) is also common among owners of LADA cars.