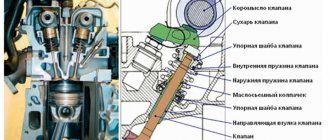
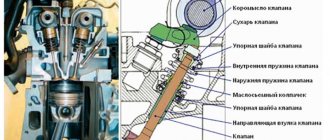
The catalyst is a unit that serves to destroy nitrogen compounds that negatively affect the atmosphere and the environment. The device turns them into harmless substances - nitrogen, water and carbon monoxide.
Depending on the year of production of the VAZ 2114, they are equipped with catalysts that meet the requirements of Euro 2 or Euro 3 (2003-2008 and 2008-2013 model years, respectively).
Removing the catalyst. Pros and cons, consumption, firmware - we reveal all the secrets
Often my blog (and my channel) receives a lot of questions regarding the catalyst, and some readers still have many misconceptions in their heads. One of them (for example) is that if you remove this part of the muffler, then it will be VERY bad for the car, it will literally stand up and refuse to go! I decided to answer all the questions at once, so today we will talk: - is it worth removing it or not (what are the pros and cons of such manipulation), what will be the consumption after cutting it out, is it necessary to flash the ECU (and what are the risks), and well a few words about “deception”. In general, it will be interesting, as usual, the video version at the end...
At the very beginning, I would like to say that this unit is NOT SOMETHING IMPORTANT for the car, but now “a bunch of stones” will fly at me, they say, what are you saying, but what about ECOLOGY? But if we put aside all the exclamations of the “greens”, then a car without a catalyst will work BETTER, CONSUMPTION will be lower, and the POWER will increase a little.
Why do you need a catalyst?
I already have an article - what is it , I won’t repeat it. You need to understand that a catalyst (and scientifically, a catalytic converter) is needed only to clean the car's exhaust from harmful emissions and make them less harmful.
In simple words, it purifies harmful gases (while glowing almost “red hot”) and “almost” harmless CO2 and N2, O2 emerge from harmful CO, CH and other compounds. This way we save the environment at least a little.
Its structure is quite simple - it is a thickened pipe, which inside has something like a honeycomb, only long and hollow. They are usually made of ceramic elements coated with noble metals (usually platinum group metals are used - iridium, rhodium, palladium).
It is because of this that it costs, to put it mildly, quite a bit, from 30 to 150,000 rubles, it all depends on the class of the car and its volume.
In order for gases to transform from toxic to less harmful, the temperature of the catalyst must be about 750 degrees Celsius, otherwise the chemical reaction will not occur. The gases that come out of a car engine have a temperature of approximately 500 - 550 degrees Celsius (which is not enough), when they pass through the catalyst, a chemical reaction occurs with the release of heat, thus heating just the right amount (750 - 900 degrees).
DIY repair
Car tuning experts usually immediately advise motorists to replace fragile, unreliable catalysts with flame arresters, because, in addition to the above functions and positive properties, they seem to extinguish the flame that arises due to the extremely powerful operation of the engine, hence the name - "flame extinguisher".
To properly replace one part with another, you need to do more than just gut the catalyst and install a flame arrester in its place. Here it is necessary to carry out more painstaking work. It is very important to skillfully select a part for your car so that it matches the brand. Today, the choice of flame arresters is quite wide, and an option suitable for one car is unlikely to fit another.
Therefore, first check with the seller for compliance with your brand and only then issue a receipt. It is precisely because of the complexity of selecting a part that many motorists make it themselves. First you need to prepare two metal tubes. The first should be absolutely the same diameter as the muffler pipe, and the other should be slightly larger. In addition, you will need metal mesh, which is usually used for washing dishes.
On the first tube we drill a hole with a diameter of 3 mm. We insert it into a larger tube, just be sure to make sure that it is clearly in the center, this is the main condition. Now we carry out welding, but only on one side. Household nets will be very useful here. You will need somewhere from 25 to 30 grids. They need to be straightened and pulled onto the first tube.
The catalytic converter is knocked out, is this bad for the car?
As I wrote above, this is simply an environmental system, and if it is not there, then the car, on the contrary, will improve its characteristics (power, consumption). To put it simply, the engine doesn’t care about this converter, whether it is there or not.
But why on many cars, if this unit fails (say, melted, clogged or crumbled), the CHECK ENGINE and the car begins to behave abnormally, traction disappears, sometimes it trots a little, and simply may not start at all.
And here, friends, everything is simple. If the catalyst is melted or clogged, then the exhaust gases cannot pass through it normally, which means that some returns back into the combustion chamber and makes the newly introduced combustible mixture less efficient. The motor is choking itself.
If there is no melting, but the “CHECK” light comes on, then perhaps it has simply worn out due to high mileage. In modern cars there are so-called oxygen sensors (lambda umbrellas), one is located in front of the catalyst, the other after and detects the presence of harmful compounds; if their percentage has increased, then the second (or also called the lower “lambda”) gives a signal that the converter is not working ( or it doesn’t do its job as it should) AND IT NEEDS TO BE REPLACED. By the way, some cars may not even start (a tribute to the environment).
Thus, by knocking out or removing it, you simply free the car’s exhaust tract from the obstacle in the form of a filter and lower its environmental standards. BUT AGAIN - THIS DOES NOT AFFECT THE RESOURCE OF THE POWER UNIT !
BUT in order for your car to drive normally, you need to upgrade to a lower environmental class (usually EURO2) or install a fake one. Otherwise, the program in the ECU will not allow you to drive normally.
Firmware for EURO2 and snag – what does this mean?
As I wrote above, the second oxygen sensor (lower lambda) controls harmful emissions. Their number is now strictly regulated by European standards, which are called “EURO”; I will not talk about EURO “0-1” now; we are interested in the second generation.
So, what is EURO2 ? It was introduced a long time ago, namely in 1996. AT that time, the cars received an innovative system, namely a catalyst. As we all know, over time it can become clogged, and the fuel then was not the same as now, it had a lot of sulfur, which contributed to the honeycombs clogging much faster, and as you and I know, the car began to choke itself. Then the engineers installed an oxygen sensor, there was only one, and it was needed to capture CO2 in the chamber in front of the catalytic converter.
If the CO2 level increased, this indirectly indicated that the catalyst was clogged (that is, a backpressure effect was manifested); the sensor sent this information to the ECU and the ignition was adjusted, namely, a decrease in the supply of the fuel mixture. Thus, the power dropped significantly, the car did not drive and the owner “willy-nilly” had to go to a service station and change this spare part.
BUT, as you and I know, the price tag is, to put it mildly, HIGH, so many owners simply removed these honeycombs and the POWER RESTORED!
But how? YES, everything is simple, the CO2 level in the chamber in front of the neutralizer dropped significantly, the oxygen sensor recorded this (that everything is in order) and the car drove cheerfully and without constraint. This suited everyone, BUT NOT ECOLOGISTS! Therefore, they introduced the EURO3 standard (now the EURO5 standard already exists). What has changed is that a second oxygen sensor (lower lambda) just appeared behind the catalyst. The principle of operation here is this : the first lambda (before the filter) records the level of harmful substances, the second (after it) should record a much lower level, because the harmful substances have decomposed.
If you remove the catalyst cells , then both sensors will record the same values (“the second one” supplies information to the ECU), thus, CHECK ENGINE will light up, the power will drop, and the car will not drive. Now this doesn't solve the problem.
What is done with firmware for EURO2? The firmware in the ECU is changed, instead of EURO3.4 standards, EURO2 standards are installed. The essence of all these actions is banal - we simply turn off the second lower lambda (only the upper one remains), the car begins to drive as expected, without underestimating the power.
But such interventions in the firmware are not entirely good. The whole point is that they don’t produce them themselves, okay, the second “lambda” is simply turned off, that is, they simply adjust the readings. Or maybe this programmer will want to put some incomprehensible algorithms into the ECU, the engine will definitely not benefit from this. You need to be very careful here.
Fuel consumption
After you have removed this filter, many are tormented by the question of fuel consumption - will it increase or not? Of course, he will fall (so I think), no matter what anyone says. Let's think logically - if there is this filter element, it represents an obstacle that the exhaust gases need to overcome, and accordingly the engine will spend more effort to push them through (consumption increases slightly). If this element is NOT present, then the “working out” will be much easier - fuel will be saved.
Of course, you shouldn’t expect any global savings, usually it’s about 3% (maximum), but it’s worth noting that consumption will drop slightly.
Popular myths
Varieties
Some people deliberately get rid of the catalyst, others deliberately ignore the clogged unit. All this caused the spread of myths.
- By removing it, the engine gains power. A misconception that arose for unknown reasons.
- The engine cannot “breathe” normally due to the catalyst. Absurd. It functions quite well if the cat itself is in working order.
- A clogged element ensures a more environmentally friendly ride. Another myth, the origin of which can only be guessed at. Rather, on the contrary, a clogged device harms nature and your car even more.
What happens if you remove the catalyst on a VAZ 2114
Messages: 1396 Registered: Aug 10, 2009, 00:00 :
Awards: 1
| Rating: 5 810 |
| Reputation: +8 |
Thanked: 122 times Thanked: 67 times
Post by Deniska » 05 Jan 2012, 09:37
fewer problems in the future if the catalytic converter becomes clogged, or the sensor malfunctions/breaks again. Well, if I’m wrong, correct me.
Messages: 12 Registered: Dec 28, 2011, 00:00 From: Tyumen Experience: 2003 Car: Skoda Octavia
| Rating: 12 |
| Reputation: 0 |
Post by Sam7287 » 05 Jan 2012, 09:51
Messages: 1113 Registered: April 29, 2007, 00:00 Car: E12 Corolla Hatch. :
Awards: 1
| Rating: 1 766 |
| Reputation: +2 |
Thanked: 1 time Thanked: 9 times
Message February_15AM » 05 Jan 2012, 09:52
Messages: 1571 Registered: Dec 29, 2011, 00:00 Experience: enough for me Car: won’t start
| Rating: 2 271 |
| Reputation: +3 |
Thanked: 51 times Thanked: 8 times
Post by Sanek_880 » 05 Jan 2012, 10:33
Messages: 6347 Registered: Feb 18, 2008, 00:00 From: Made in USSR Experience: 1995 Car: Land Rover, Suzuki In :
Awards: 1
| Rating: 15 482 |
| Reputation: +26 |
Thanked: 93 times Thanked: 106 times
Post by Renault » 05 Jan 2012, 10:54
Messages: 242 Registered: June 21, 2011, 00:00 From: Tyumen Experience: 2002 Car: FF2
| Rating: 252 |
| Reputation: 0 |
Post by Diesel85 » 05 Jan 2012, 15:29
I was faced with the fact that one winter one spark plug failed. all the unburnt fuel began to burn out in the catalyst, all the honeycombs melted and clogged, the catalyst itself became red-hot and burned out. The car could easily burn out from this. The car had only 6 thousand miles. I found out that the warranty on the catalyst is only 30 thousand. The maintenance was done by non-officials and the car lost its warranty. In general, we knocked out the remains of the honeycomb from the catalyst, welded the hole, and replaced the program. As a result, the car became much faster, I compared it with a friend’s car, he also has 14 with a catalyst, mileage is 20 thousand.
Added after 6 minutes 26 seconds:
Regarding gasoline and noise, this is all nonsense. With the new firmware it has become more economical. the sound began to work exactly the same, although not large particles of ceramic honeycomb residues got into the muffler can and did not rattle much when the engine was idling. I didn’t bother removing the muffler because of this. Over time, the rattling disappeared.
Planned replacement
The catalyst resource ranges from 60 to 100 thousand kilometers. During operation, the ceramic honeycombs become clogged with waste and the VAZ 2114 neutralizer must be replaced.
If you refuel with low-quality gasoline, the catalyst will fail much earlier. All fuel filters will also deteriorate.
Over time, the carrier breaks down and the internal pressure of the exhaust system increases. Most of the exhaust gases return to the engine. In addition, there are factors other than the age of the node that affect its condition.
How to determine that the catalyst has become unusable
Typically this can be seen, heard or even felt through the sense of smell:
- So, if the ceramics crack, it begins to rattle in the metal case.
- In addition, exhaust gases acquire an unpleasant odor while driving if the catalyst is faulty.
- As for the color of gases, they also change dramatically. Instead of the usual color, gases with a faulty catalyst become like black soot.
- Engine power is also reduced, especially on inclines.
Causes of malfunctions
The main reasons causing catalyst malfunction include:
- Poor quality fuel.
- Faulty oxygen sensor. In this case, too rich a mixture destroys the neutralizer.
- Leaks of oil and lubricating fluids. Liquids entering the working chamber.
- Prolonged operation of the engine in idle mode.
Signs of a faulty catalyst
- Loud noises from broken ceramic honeycombs.
- A characteristic smell in the cabin and from the exhaust gases released.
- Black exhaust color.
- Reduced engine power. This is especially noticeable on the rise and during acceleration.
- Unstable engine speed.
- Sometimes the case overheats so much that it begins to melt, and other parts behind it become deformed.
With extreme driving styles and/or poor road conditions, ceramic honeycombs break before their normal service life expires.
Diagnostics
For diagnosis you will need:
- tools for removing the lambda probe;
- pressure gauge;
- remote pyrometer.
A pressure gauge is installed in place of the lambda probe and the pressure is measured with the engine running. If it is more than 0.5 atm, there is most likely a problem in the converter.
Another way to check is to measure the pipe temperature with a remote pyrometer. If the converter is operating normally, the section of pipe upstream of it will be hotter than the section downstream of the catalyst. When the temperature is the same, this confirms the destruction of the ceramic carrier and the violation of flame retardant functions.
If a malfunction is detected, the catalyst on the VAZ 2114 must be immediately replaced.
Breakdowns and their signs
Typically, this element begins to “strange” when it travels about 150 thousand kilometers. That is, this is more likely an age-related problem with the car.
Standard and Modified
Typical signs that the catalyst is clogged are:
- The car's dynamics deteriorate significantly and noticeably;
- The engine starts with problems;
- There is a characteristic smell of sulfur in the cabin;
- The engine is unstable at idle.
If the car stops driving normally, it is advisable to immediately check the condition of this device. Alas, this cannot always be done in a garage environment, since special equipment and devices are required. But there are still two ways.
- Replace the lambda probe with a pressure gauge. Start the engine and check the pressure. If it is more than 0.5 atmospheres, things are bad.
- In the second case, you will need a remote pyrometer. If the catalyst is working normally, the temperature of the pipe before it will be higher than after it. But at the same temperature, this indicates the destruction of the honeycomb and a violation of the flame extinguishing function.
The second method allows you to obtain indirect data, so the pressure must be checked in any case. If a breakdown is detected, the catalyst must be replaced.
Removal and replacement (16-valve engine)
On cars with 16-valve valves, the catalyst is located in the engine compartment next to the exhaust manifold. The node must be looked for behind the cylinder block. If you know how to remove the catalyst for a VAZ 2114, you can do the work yourself, but you will have to remove the fuel rail.
There are 2 lambda probes on the unit. One is located on the catalyst. It is used to regulate the composition of the fuel mixture. The second probe is mounted behind the assembly on the flange and is called the “environmental” probe. If this probe is missing, the sensor generates an error, the injection system is rebuilt, and thrust increases with fuel consumption. The sensors are removed from the assembly. Having dismantled the unit, install a new one and connect the sensors.
Budget replacement options
In addition to installing a new standard unit on a 1.6 engine, replacing the catalyst on a VAZ 2114 is possible in the “budget option”. To do this, use a zero-resistance catalyst (“spider”). There are two types of spiders - 4-2-1 or 4-1. Option 4-2-1 is the transition of four pipes into two, which are connected into one pipe. Option 4-1 differs from the first in that four pipes coming from the engine are immediately connected into one pipe.
If the spider is designed for one probe, the ECU is flashed from Euro-3 to Euro-2. On such spiders, only the installation of a flange probe is provided. To simulate an injection probe, you need to install an extension cord (wire and female-male connectors).
If there are two sockets on the spider, the injection probe is mounted in its original place. Instead of the second probe, they install a decoy for the ECU. In this case, there is no need to reflash the ECU.
Instead of a catalyst, some owners of cars with 8-valve engines install a flame arrester. The unit can be purchased at a car store or made yourself. The oxygen sensor is installed before the neutralizer, so the flame arrester will not affect its readings.
If your financial capabilities allow, it is better to replace the catalyst with a new standard unit. The environmental situation is constantly deteriorating, and the total amount of harmful emissions depends on the actions of all car owners.
To assemble a flame arrester yourself, you need two tubes, one with the same diameter as the muffler, and the second of a larger diameter, and 25-30 metal mesh for washing dishes. The tubes are welded on one side, the mesh is put on a tube with a smaller diameter and the tubes are welded on the other side. For aesthetics, the flame arrester can be painted.
Another budget option is to dismantle the ceramic honeycombs in the faulty converter. The central part of the part is cut out by welding, all the honeycombs are knocked out and the seams are welded. If you drive with such a restored part, it will always be accompanied by a loud noise.
Error (check) lights up after installing the catalyst
This happens when you remove the catalyst. If, for example, you had two sensors - you installed one, or even if you installed two (spiders are different), then different readings appear, which is why the error occurs. It is necessary to reprogram the ECU for Euro-2 (for one oxygen sensor).
Sources
- vaz-2114-lada.ru/2014/06/katalizator/
- zen.yandex.ru/media/all_auto/rossiiskaia-reznia-katalizatora-chto-vnutri-posle-183-000-km-probega-5d56e02cc49f2900ace743f3
- masteravaza.ru/vozdushnyj-filtr-i-sistema-vypuska-otrabotavshih-gazov/katalizator/zamena-katalizatora-na-vaz-2115-97
- drive2.ru/l/288230376152139928/
- ladaautos.ru/vaz-2115/opisanie-katalizatora-vaz-2115.html