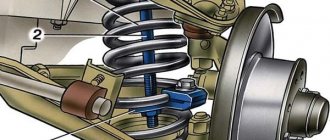
The question of how to check a spring is often of interest to car owners only when the car “sags” even with a small load, or even without it. However, such a check of the suspension springs should have been done only when the first symptoms of their wear appeared. It is best to do diagnostics in a car service center on a special stand, but the simplest check of the condition of the springs can be done in a garage with your own hands. This does not require a special tool, and the procedure is accessible to almost everyone.
When to change suspension springs?
One of the important elements of the suspension are springs. Determining when to change suspension springs is not difficult. You can carry out this procedure yourself or contact a service station.
If the springs fail while driving, every hole or bump on the road will be felt, vibrations, extraneous noises, and knocks will appear. In addition, the movement of a car with such a breakdown becomes unsafe for road users, so sagging or broken (with a broken coil) springs should be replaced immediately.
Spring sizes — Lada 2104, 1.4 l., 1997 on DRIVE2
Perhaps this article will be to the taste of some car enthusiasts!
Brief technical characteristics of springs
Front suspension springs
Spring model: 2101 Rod diameter, mm: 13.1 Outer diameter, mm: 116.3 Number of turns: 8.75 Length mm: 360
Spring coating: epoxy, black enamel
Spring model: 21012 Rod diameter, mm: 13.5 Outer diameter, mm: 117 Number of turns: 8.75 Length mm: 360
Spring coating: epoxy, black enamel
Spring model: 2121 Rod diameter, mm: 15.2 Outer diameter, mm: 120.4 Number of turns: 7.3 Length mm: 278
Spring coating: epoxy
Spring model: 2108 Rod diameter, mm: 12.9 Outer diameter, mm: 149.6–151.6 Number of turns: 7 Length mm: 383.5
Spring coating: epoxy, black enamel
Spring model: 2108 European Rod diameter, mm: 12.9 Outer diameter, mm: 149.6–151.6 Number of turns: 7 Length mm: 364.5
Spring coating: epoxy, black enamel
Spring model: 2112 Rod diameter, mm: 13.2 Outer diameter, mm: 151.2 Number of turns: 7 Length mm: 383.5
Spring coating: epoxy, black enamel
Spring model: 1111 Rod diameter, mm: 10 Outer diameter, mm: 94–95 Number of turns: 9.3 Length mm: 316.8
Spring coating: epoxy, black enamel
Rear suspension springs
Spring model: 2101 Rod diameter, mm: 12.4 Outer diameter, mm: 127.5 Number of turns: 9.3 Length mm: 434
Spring coating: epoxy
Spring model: 2102 Rod diameter, mm: 12.4 Outer diameter, mm: 127.5 Number of turns: 9.3 Length mm: 455
Spring coating: epoxy
Spring model: 2121 Rod diameter, mm: 12.7 Outer diameter, mm: 127–129 Number of turns: 9.3 Length mm: 434
Spring coating: epoxy
Spring model: 2108 Rod diameter, mm: 11.2 Outer diameter, mm: 107.2 Number of turns: 11.5 Length mm: 418
Spring coating: epoxy
Spring model: 2108 European Rod diameter, mm: 11.2 Outer diameter, mm: 107.2 Number of turns: 10.5 Length mm: 381
Spring coating: epoxy
Spring model: 2110 Rod diameter, mm: 11.6 Outer diameter, mm: 108 Number of turns: 10.5 Length mm: 381
Spring coating: epoxy
Spring model: 2110 European Rod diameter, mm: 11.6 Outer diameter, mm: 108 Number of turns: 11.5 Length mm: 403
Spring coating: epoxy
Spring model: 1111 Rod diameter, mm: 9.7 Outer diameter, mm: 99.7 Number of turns: 9.5 Length mm: 353
Spring coating: epoxy, black enamel
Signs of sagging springs
There are a number of factors that will help determine whether the suspension springs are faulty, for example:
- Knocking noise while driving.
- Strong vibration.
- Reduced ground clearance without load
- Car sagging even from a small load.
- The car rolls to one side.
All of the above problems indicate that the suspension springs have failed. It is also worth carefully inspecting the springs: any area of corrosion is a likely site of future failure.
Where to buy Patron suspension springs?
Today, the market offers a wide range of auto parts from various manufacturers, which makes it difficult for consumers to decide on a brand and choose a truly high-quality product. The prices for original spare parts are quite high, and not every driver can afford to purchase them. Among the available alternatives, which are not inferior in quality to the original ones, PATRON spare parts, our own brand, stand out. You can purchase Patron suspension springs, as well as other automotive components, in the company’s stores, as well as at points of sale from official dealers of the brand.
Patron auto parts undergo strict quality control during the production process, which is confirmed by numerous certificates. Suspension springs of this brand are made exclusively from high-quality raw materials in compliance with all requirements for production technology. Car owners who purchase PATRON parts note their reliability and wear resistance.
From the outside, checking a car's suspension seems like a complex process that requires global technical knowledge and equipment proficiency. In fact, it is possible to check the suspension yourself - this does not require equipment or complex instruments. We will tell you in this article how to properly check the suspension yourself, and what conclusions you can draw after checking.
avtoexperts.ru
It's no secret that the suspension experiences serious shocks due to the quality of the roads. And in order to somehow minimize the impact, springs are installed. They affect not only the main parameter, such as the height of the body above the ground, but also allow you to keep the car at a practically specified height, even taking into account the cargo taken on board. In addition, there is an opinion that the effect of springs on the suspension as a whole is favorable, and the handling of the car improves.
Remember that the design of all springs is generally identical, the only differences that may be are the stiffness indicator and the type of shape of the products themselves.
Keep in mind that depending on the type of part, roll in turns may exceed the permissible 3-4 degrees. With properly selected springs, this indicator remains at a level of no more than two degrees. Therefore, it is very important to choose the right element that will correspond not only to the nature of your driving, but also to the basic requirements of the manufacturer for a particular model.
Also, don't forget that part of choosing the right spring depends on where exactly it is being installed. After all, there are two placement options - on a stand and separately.
For example, often, when the shock absorber and spring are located separately, barrel-shaped and conical shapes are chosen.
But for installation on racks, preference is given to coil springs. The true reason for this “policy” of manufacturers is not known, but there is an opinion that this format is due to the fact that the racks are usually installed at right angles. And when the arrangement is separate, a small angle is provided, and in this case, the cone and “barrel” make it possible to “eliminate” the tension when the spring “plays” on bumps and when sagging due to overload.
In general, you can notice this pattern: when a joint pair of struts and springs is installed, the main emphasis is on rigidity and ground clearance. But, you must also take into account that stiffer springs can be used. Regarding the separate location, shock absorption occurs along several trajectories, depending on the modification. Which is why many claim that the split type is more suitable for driving on bumpy roads and in the city; the cabin is comfortable, because in this case, the suspension handles multidirectional impacts better.
Hardness, how to determine?
First, let's establish what a spring is? This is a mandatory component of the suspension, which is presented as a certain elastic element. It provides mitigation of impacts and jolts, including during sudden braking and starting. The purpose of the spring is to return the wheel to its original “position” as quickly as possible after hitting an obstacle.
A part that is too rigid significantly impairs the car's handling, especially on rough roads. However, the advantageous side of increased rigidity is greater safety when driving at high speeds. That is, it does not allow the body to sway as much as if it were too soft. The latter cope with almost all potholes without discomfort for the driver, but with such springs it is difficult to take turns.
Remember, there are several main factors that affect stiffness. Knowing them, you can independently determine the type of your own element installed on the suspension. So:
1. The diameter of the rod itself. Remember an important rule: the thicker the rod, the stiffer the part.
2. Spring diameter on the outside. The larger the diameter, the lower the actual stiffness.
3. Form. There are several main types: conical, cylindrical, barrel-shaped. Each variety has its own characteristics and characteristics. There are also combined ones.
4. Number of turns. The rule is this: the more turns, the less rigidity there will be.
Hardness is determined quite simply. In most cases, the manufacturer independently applies markings that make it clear which class the product belongs to.
Remember that the yellow marking indicates a length of up to 240 mm. But, basically, all the indicators that are required to calculate stiffness are on the product.
If no markings are found, the indicator can be calculated as follows. So, prepare scales (regular floor scales), a wooden block, a ruler, and the product itself. You need to place the block on the scale, but remember that the width of the board must be greater than the diameter of the spring. Next, we take the second board and press it on top and measure the length of the product, naturally, without taking into account the boards. Either independently or using a special press, the spring must be compressed to a certain level. As a rule, this is 40 mm. Record information from the scales. Next, having the initial length in the expanded and compressed positions, we calculate the difference. Next, you need to divide the resulting weight after compression by the difference, thereby obtaining a stiffness indicator.
There are more complex methods of calculation, but it’s not worth talking about them, because at least two more values are required, which can be derived if you know Hooke’s formulas and laws, as well as the theory of proportionality. For an ordinary driver, this method of calculation is superfluous; it can be found out much easier.
Resource, and which ones are better to choose?
As a rule, among the most popular queries in search engines is what is the mileage of springs, and which ones are better to choose? It is difficult to judge which ones are better, because each motorist has his own preferences in this regard. Some people like to drive fast and have strict safety requirements, while others prefer comfort. Everything is individual, moreover, today there are a huge number of manufacturers who can offer universal springs, including so-called adjustable ones.
What, in principle, should be understood by the word regulated? It just seems to you that everything is simple, but they can still differ from each other. There are two types:
• With an adjustable “nut”, which is screwed onto the cylinder and allows you to either increase or decrease the rigidity depending on the “twisting”.
• With an adjustable spacer, in principle, many of these two points are not even separated
What resource? It is difficult to answer in the affirmative about the service life, because everything directly depends on the quality of the roads. In some places the springs last 100,000 km, but in others they don’t last even 10,000 km. In general, it can be noted that the greater the rigidity, the more durable it is, and vice versa. The average “mileage” rarely exceeds 50,000 km.
Malfunctions and their symptoms
There are not many faults as such; in fact, the design part of this element is not complicated. The following types of problems are divided:
• Bar breakage at the edges.
• Trivially “tired” metal.
In general, that’s all, there’s nothing more to add. Either the spring sagged due to frequent overloads, or the coil burst, that’s all.
What are the signs of trouble? A wide range of features can be noted here:
1. Reduced lumen (clearance).
How to check the front suspension
Most cars have a standard McPherson front suspension. The most expensive part of the suspension are the struts and shock absorbers. In terms of difficulty of replacement, the following are the silent blocks of the stabilizer and levers. The easiest and cheapest thing to change is the ball joints of the front suspension.
When checking the front suspension, first of all, inspect the anthers and rubber covers of the parts, and then proceed to inspect the silent blocks, balls and all of the above. Inspect the mounting bolts and tie rod ends. If you find a part whose cover is damaged, you will need to replace the part.
Carefully inspect all rubber seals; they should not have mechanical damage. Separately examine the parts adjacent to the body - here you need to inspect more carefully due to poorer visibility.
The shock absorber will show oil leaks - the first signs of a malfunction. They can be noticed before sounds occur when the car rocks. If the car swings instead of the vibrations being dampened, this will also mean wear on the shock absorber, but at a more advanced stage - again, replacement is required.
Why do shock absorbers leak?
There can be several reasons for a leak. Contrary to popular belief, the least likely of these is the advanced age of the shock absorbers. According to the regulations, they are supposed to be changed every 60-80 thousand kilometers. However, this only applies to those cases when the car is operated on normal roads. If we take into account the state of our roads, then “old age” or even death of the racks can occur at any moment. Even on the day of purchase and installation of new ones. So, if the shock absorbers on your car have served for more than 80 thousand kilometers, this does not mean at all that they have leaked from old age.
A more likely reason why struts leak is due to excessive loads on the suspension. Sometimes just one hole is enough for the shock absorber to “cry”. This happens because the working fluid has nowhere to go during a sudden movement of the piston. Accordingly, it looks for weak spots in sealing gaskets and oil seals, and flows out through them.
The next reason why car struts leak is mechanical wear as a result of the destruction of the anthers. They protect the mirror surface of the rod from abrasives in the form of dust, dirt and sand. If the anthers are cracked, destroyed, slipped out of place or are completely absent, then the stand wears out very quickly, losing its tightness. It is clear that as a result of this, the shock absorber may begin to leak even under minimal loads. That is, as they say, out of the blue.
Another possible reason why shock absorbers leak is a large load on the cold suspension. This happens in winter. Under the influence of negative ambient temperatures, the working fluid thickens and its fluidity decreases. As a result, during movement, such oil cannot be normally distilled by the piston from compartment to compartment. That is, again, it has nowhere to go, and it looks for weak points to leak out.
Trivial and obvious reasons for shock absorber leaks include careless driving, inattention, and lack of experience. For example, not all motorists know how to properly drive over potholes and other irregularities on the road. That’s why for some, the suspension lasts for years even on bad roads, while for others it requires repairs almost every spring. Much depends on the quality of the racks. Very often, car enthusiasts, trying to reduce the cost of maintaining a car, buy non-original spare parts, which a priori are not required to last long. Even on ideal roads.
Determine the problem by eye
When the springs are heavily worn, they sag, and all that is required in this case is to inspect the car, paying attention to its fit. The car is lower than it should be - a sure sign of “fatigue” shock absorber springs. This also makes it impossible to adjust the wheel camber.
Ball joints are checked in an inspection hole; this is somewhat more difficult, as it requires the ability to look under the car, as well as the presence of a mount. Press the lower control arm bushings and check how they move up and down. If there are no backlashes, and the rubber on the parts is intact, then everything is in order and you don’t have to worry.
INCREASING THE LENGTH OF BRAKING DISTANCE
Frequent abnormal operation of the ABS and ESP systems are one of those warning signs of suspension failure that should not be ignored. As soon as a car starts to do something like this due to excessive pitching and swaying, you need to understand that this is directly related to a decrease in the effectiveness of braking and other control actions of the driver. Which in turn is a direct threat to security. The results of many tests show a significant increase in the braking distance of a car if its shock absorbers are worn out. During emergency braking, even on a flat road, the dynamically unloaded wheels of the rear axle perform intricate dances - hence the loss of wheel contact and a decrease in braking force.
Driving and on the move
Some defects are diagnosed while driving, or simply from behind the wheel in a static position. Problems with the steering rack are diagnosed by turning the steering wheel to the side and rocking the rack. Usually the cause of problems with this mechanism is wear of the guide bushing.
Steering rods and ends are also checked by moving the steering wheel, but not once, and from side to side. In this case, you will need an assistant, since while moving the steering wheel you need to hold on to the steering tips and rods - they should not play. If there is play, it means the tips are faulty and require replacement.
The easiest way to determine the condition of the hub bearing is while driving - in the event of a malfunction, it emits a loud and uniform hum; it will be difficult not to hear it even with good sound insulation of the car. The condition of the wheel bearing can be determined by hanging it: spin the wheel, or swing it at the top point, and check for play.
Since you have taken to studying the car's suspension seriously and asked the car seller for a test drive, test the outer CV joints that make a cracking noise when turning sharply with acceleration. Carry out a maneuver and listen to how the car reacts.
How to check the rear suspension
The main part of the components and assemblies is concentrated in the front suspension, so it is easier to check the rear suspension. On most budget cars the rear suspension is dependent, its most expensive part is the struts; on medium (budget) cars they last about 100 thousand kilometers, after which they begin to “get tired”.
There is nothing else significant or critical in the rear suspension, except for the silent blocks, which are practically eternal (again, look at the condition of the rubber bands). If the rear suspension is independent, its design is somewhat more complicated, but the essence does not change - apart from the struts and silent blocks, there is nothing fatal, but in an independent suspension they wear out faster, and this is more noticeable.
It is best to check the rear suspension together with the front during a test drive; here the sounds and behavior of the car will best tell you about the situation - whether something “clunks” or not, and how it absorbs it - whether it sways on bumps or not. If the car rocks on uneven surfaces not only up and down, but also sideways, this indicates that the suspension is damaged and repairs are urgently needed. This also means that the car was not looked after or looked after at all, and it is better not to buy such a car.
Installation Tips
- Is it possible to install parts of different classes?
Remember that the springs on the suspension must be of the same class. Let’s say you installed A-class parts on the front suspension, which means you also need to install “A” class on the rear suspension.
If a similar class is not available for the rear suspension, then in exceptional cases class “B” is assigned to the rear suspension.
If B-class springs are installed on the front suspension, then class “A” springs cannot be installed on the rear suspension.
Install suspensions of the same class on the left and right sides of the same axle.
- What springs are better to install on a VAZ 2107?
Before changing parts, make sure that it is really necessary. You can check it in the following way: standing at the front of the VAZ 2107, swing the body down. If it quickly rises to its original position, there is no need to replace the springs; they are in good condition. If the body does not rise and continues to sway, then replacement is necessary. In the same way you can check the rear suspension of the VAZ 2107.
To improve the aerodynamics of the VAZ 2107 and improve the sensitivity of the steering wheel, it is recommended to install stiffer springs than the original ones. You can buy those designed for VAZ 2104, cut off one turn. It is imperative that on a VAZ 2107 you need to change two at the same time, otherwise the car will lose stability on the roads.
It is not recommended to install reinforced rubber gaskets on 2107, because the spring will break through.
- Will Niva springs fit on a VAZ 2107?
If you want to make a sports tuning on the VAZ-2107, the suspension is made more rigid, this improves the quality of handling without reducing the level of comfort.
The rear springs are stiffer than the front ones. The factory ones are too soft, and the car quickly loses control, the bottom gets scratched on the road surface. To increase the stiffness of the suspension, it is recommended to install Niva springs on the VAZ 2107.
- What springs are better to install on a VAZ 2110?
On the VAZ 2110, the front spring often breaks due to poor quality roads, so it needs to be replaced. Moreover, you can do this yourself, without contacting a car service. All that remains is to find out what is best to choose from the range offered for the 2110.
On the front suspension of the VAZ-2110, as standard, 2108 springs are installed, on the rear suspension - 2110. In the absence of original parts, car enthusiasts are advised to install SS20 highway, the car rides smoothly and is stable when cornering.
- What springs are best to put on a Priora?
If the springs on the Priora have sagged, it is recommended to install new original ones from VAZ. Choose only the class depending on the goals of your tuning. Class "A" is more stringent. In the absence of the original one, according to car enthusiasts, it is better to install a kit with a lowering Eibach Pro-Kit (-30 mm).
- What springs are better to install on a VAZ 2114?
The VAZ 2114 suspension is quite durable, and the need to replace parts occurs quite rarely. Therefore, not all car owners of 2114 cars know what is best to choose from the wide range offered on the markets.
Sometimes springs from 2112 are installed on a VAZ 2114, they are a little stiffer, designed for a larger weight of the car, so they raise the 2112 slightly - by 2-3 cm, which means that in this way you can increase cross-country ability. If, on the contrary, there is a desire to lower the car, then it is recommended to purchase an Eibach, with the front ones being -5 and the rear ones -7, so that the car does not ride up.
So, the choice of springs for VAZ is quite wide, the main thing is to choose the correct stiffness characteristics according to the load on the car and operating conditions. You will find a variety of advice on forums and blogs. Of course, it is better to first consult with specialists. Refusal of original parts in favor of other manufacturers may be dictated by the desire to improve the driving performance of the car, but be sure to compare the cost of tuning and the result obtained.
Main suspension parts
It is best to check the main components and parts of the suspension while driving; the sounds will tell you in detail whether there are any malfunctions. The car needs to be driven over uneven surfaces, such as rails or bumps, but without fanaticism, so as not to damage the vehicle.
The main components, the condition of which you need to know:
- Shock absorber - serves to dampen vibrations. If the car rocks strongly, the shock absorber is faulty.
- A spring is an integral part of the shock absorber; if it sags or bursts, the car becomes significantly lower than the factory setting.
- The ball joint is mounted on the lever on one side, and on the steering knuckle on the other. Responsible for turning the steering wheel.
- Lower arm – attached to the body at two points, ensures the operation of the suspension. There are silent blocks at the attachment points to the body.
- Stabilizer link - connects the stabilizer and the strut, thus connecting it to the suspension.
- Steering rack - transmits force from the steering wheel to the steering knuckles. When turning the steering wheel, there should be no play and no extraneous sounds.
The suspension itself will tell you about the main points, but if you want to know everything in detail, then it’s better not only to look under the car and ride it, but also contact service specialists who, using a lift, will be able to examine the condition of the suspension parts and tell you exactly what there is a problem.
What is ecoclass
Due to possible restrictions on the environmental class, the motorist is advised to find out which category his car belongs to. This will allow you to freely pass through customs checkpoints when crossing state borders, or you will immediately understand that there is nothing to do abroad with a car with an assigned EC.
First, you need to understand what the environmental class of your car means and what information a mark like Euro 4 provides.
Specialists deal with issues of environmental friendliness of vehicles. Environmentalists collect information and statistics that clearly demonstrate the level of danger and harm from automobile exhaust gases. According to experts, one car emits 4 kilograms of exhaust per year.
European countries, or rather their leadership, did not ignore this problem, and therefore developed the concept or definition of an environmental class for a vehicle. That is, each vehicle has its own safety class determined depending on how much it pollutes the environment. In this case, there is a ban and certain restrictions on the current environmental class if the car no longer meets the updated established current standards.
Within the framework of the adopted Geneva Convention, special environmental regulations were developed. And similar norms have been implemented in almost all countries of the world. To obtain permission to import cars, the vehicle must meet a certain environmental class. This is already determined by each country individually.
New standards were established in 2021 and are currently in effect. They provide:
- no more than 0.05 g/km CH;
- up to 0.8 g/km CO;
- no more than 0.06 g/km NOy.
All this complies with standards designated as Euro 5. At the same time, automobile companies continue to produce models whose eco-class complies with the requirements of Euro 4 and Euro 3. Anything below this value has been discontinued.
The task of the EC is to tighten current requirements for the level of environmental safety of operating vehicles. Such measures are aimed at preserving the environment. After all, exhaust is one of the most dangerous and harmful pollutants in the world. To combat this problem, environmental standards were developed, divided into classes.