12.12.2012
In almost 100% of modern cars, the body is used as a single source of electrical energy. The car body is like a universal wire with a negative charge for all consumers of electricity. That is why the body is called the painfully familiar term “mass”. Why “painfully familiar”? Yes, because if somewhere the contact with the mass is either poorly secured or oxidized, the inexplicable begins. Let’s take the first example we come across: the sore subject of the first and second Samaras is the blinking of yellow and red headlights, etc. I have already analyzed this situation in the article: why the headlights do not light up, where I made a “mass”, as the main reason for unstable operation. But the headlights are a small thing compared to the performance of the engine and the electronic engine control system (ECS). In this article we will look at the weak “mass” points on the VAZ 2114 2113 2115 with 1.5l, 1.6l engines.
ECU weight
A reliable ECU ground is very important for the proper operation of the engine management system and the engine as a whole.
It would seem to be a primitive and reliable design that can serve well for years. But in reality this is far from the case.
It is very difficult to list all the possible problems that can arise due to poor ECU mass, since it can affect anything. But the main problems can be divided into two points:
- Incorrect collection of information from engine control system sensors. Personally, I had to deal with incorrect MAP sensor readings. It gave inflated barometric pressure readings precisely because of the poor weight of the ECU.
- Since almost all modern engine control units are able to adapt to real operating conditions, as a result of incorrect collection of information from sensors, adaptation leads to engine malfunctions. This is why for many, after resetting the adaptations, the engine begins to work much better. But then the problems return as the ECU adapts again. And again this does not happen quite adequately.
Frequent malfunctions of the VAZ electronic control unit
Considering that the controller is a complex electronic device, failure of the ECU cannot be ruled out. As a rule, the causes of ECU malfunction can be different, ranging from mechanical damage to software failures.
For example, a common cause of breakdowns is overheating or liquid ingress. As practice shows, on the Lada Samara the ECU is located near the heater radiator. It is not difficult to guess that a radiator leak and coolant entering the controller often disables this device.
In this case, the check engine light does not always light up on the panel, but the engine malfunctions. In such a situation, when no other causes have been identified, what is needed is not diagnostics of the engine and systems, but professional diagnostics of the car's ECU, which can only be performed by an experienced specialist. Often, after checking, the unit may need to be replaced, since ECU repair is often not recommended.
Where is the ECU ground located?
The ECU mass is usually arranged like this. Separate ground wires are removed from the ECU connector and connected to the engine via the starter mounting bolt. Ground wires are usually black.
In the photo, the thick wire is from the battery, and the thin wires are from the ECU and speed sensor
Everything is simple and reliable. But in reality, over time, the voltage begins to drop in this section of the circuit, slowly but surely, disrupting the operation of the system.
Therefore, this unit must be periodically checked and maintained. We will look at how to do this further.
Troubleshooting
For uninterrupted operation of the battery, the system must be equipped with good quality wires; in this case, copper wires are the most suitable, since they have the best characteristics when operating under voltage.
The thin positive wire coming from the generator must be replaced with a thicker wire.
To protect the existing mass and ensure longer and more trouble-free operation, it is necessary to treat all existing connections and terminal contacts with a special lubricant that has an anti-oxidation function.
You can strengthen the mass by placing additional mass near the generator. Of course, you should not use a thin negative wire to connect to the car body; it is better to use a thick wire. The result will be better, and if problems arise with the main wire, the additional one will be able to start the car, and again you will not have to listen to the clicking of the relay.
As a result of the procedures performed, the car will start more confidently. We will eliminate the problem of frequent battery discharge, which will avoid the loss of much-needed volts for the car and, as a result, ensure the most stable and sufficiently high voltage coming from the generator.
The article was written thanks to the “Crafts” website. This is a creative portal that contains the best master classes on needlework, practical tips on the house, knitting, embroidery, decoupage.
Weight between engine and body
Line “31”, popularly called “ground”, “minus” or “negative circuit”, is very important for a car. And not only for electrical equipment, but also for many other systems, including the engine or automatic transmission.
Almost all cars have a single-wire on-board network system and the role of the “minus” in this circuit is played by the metal parts of the body. This greatly reduces the number of wires and reduces the cost of the car.
It turns out that all participants in this chain have their own connection to the body - instrument panel, headlights, ECU, engine, etc.
Despite the visual integrity of these connections, over time, due to oxidation and corrosion, the contact slowly and imperceptibly deteriorates, which leads to voltage drops when powerful consumers are turned on or disruption of the system.
I would divide the mass connections into main and local. Let's say that the connection of the head light masses is local and if this connection is disrupted, only the head light will suffer. But if the ground contact from the battery to the body is broken, the entire on-board network will suffer, and this may cause problems in the operation of the engine and other important components and assemblies.
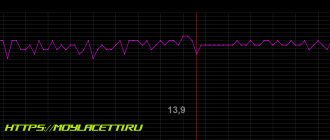
This is how the voltage of the on-board network with problematic masses looks like on the diagnostic graphs
And here is the graph after mass prevention of battery - engine - body
Therefore, a reliable engine-body mass is very important for the proper and trouble-free operation of the entire vehicle.
And the mass of the ECU - engine is even more important, since the voltage in the engine control system does not exceed 5 V. Therefore, this further encourages owners of cars with an engine management system to take the issue of mass more seriously than owners of carburetor cars, where the voltage is 12 -14 B. Because the lower the voltage, the greater the damage from losses in the circuit.
In general, the ground chain must be maintained in perfect condition. It's like an axiom.
Next, let's look at where the engine-body mass is located and how to check it.
Burnt out light bulb
The obvious reason for side lights not working is a burned out bulb. You can determine the condition of a part visually and by sound. In a complete lamp, the tungsten filament in the body must be intact and taut. A burnt part makes sounds when shaken. The price of new lighting parts is cheap, so it is enough to replace them with serviceable ones (possibly diode ones).
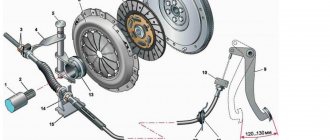
Where is the mass of the engine - battery - body
On most cars, the engine-body mass has a primitive appearance and is made of two pieces of cable connected together by crimping on the negative terminal of the battery
This crimp connects two wires. One goes to the engine and is secured with the starter mounting nut...
...and the second one on the body in the area of the left wing
It would seem that this is the simplest and most reliable chain that will serve well for years. But this is not at all true and it’s all to blame for the weak points in this design, which do not withstand the test of atmospheric influences.
What else is important to know?
If you decide to install such a scheme, you should first consider several important points.
- If there are devices and instruments in the car that require adjustment, in the event of a power failure, they will need to be periodically restored. This usually concerns setting the time, date, etc.
- Opening the ground does not reset the odometer and does not reset the ECU settings, so there is no need to worry about this.
- If your alarm system has an autonomous siren, it may be triggered in the event of a ground fault.
- If the alarm does not have an autonomous power source, disconnecting the battery leads to automatic deactivation of the security system. It just won't work.
- On vehicles with an injection type engine, if the ground is disconnected, the power to the controller is also turned off. This leads to the deletion of all accumulated information.
- Periodically check the condition of the contacts and take resistance measurements. It is better to lubricate them with lithol, and also renew the lubricant.
- Some experts agree that it is better not to use the switch for cars manufactured after 2000. If it accidentally operates while the ignition is on, the immobilizer may become unstuck. The motorist will lose the ability to access his own car. To restore work, you need the help of specialists and an impressive amount of money.
- Disabling the mass leads to the loss of previously made settings in the multimedia system.
All this directly indicates that not everyone needs a mass switch and not always. And if you use it, then only when absolutely necessary.
Think carefully about the feasibility and necessity of using a car battery disconnect switch. Sometimes it makes sense to make a device yourself. But most are of the opinion that it is better to use factory solutions and involve experienced auto electricians. The choice is yours.
How to check mass on a car
In fact, only a small group of motorists pay enough attention to this issue. Others begin to think about it when, when the cooling fan or headlights are turned on, the engine speed begins to sag, or when the rear window heating is turned on, the engine begins to tremble, transmitting vibration throughout the body.
But even at this stage, many limit themselves to a banal inspection and tightening the ground connection nuts on the engine and body. Everything is screwed down - that means everything is in order.
Then the car begins to jerk for no apparent reason, idle speed freezes, misfires, security system glitches, and so on, until the starter fails at the most inopportune moment. But even here, many will not go check the masses, but will run to the store for a new starter. After all, the wire to the starter is intact and there is voltage, but it, a radish, does not turn.
Replacing the starter, of course, does not help. As a result, the still-living battery goes into recycling and the situation seems to have improved, but after a couple of days the starter fails again and you begin to believe in brownies and otherworldly forces that have nothing better to do than cause damage to someone else’s car.
But, fortunately, reason wins and the advice of a good man is remembered - to check the masses.
Again, what's so difficult about this? It is necessary to check the resistance from the engine to the body.
Power supplies
Fuses and relays VAZ 2114 2115 2113
On the vast majority of modern cars, the power source is a three-phase alternating current synchronous generator driven by the main engine; three-phase alternating current from the generator is supplied to the built-in three-phase rectifier and voltage regulator circuit - in modern cars the voltage regulator is built into the generator housing. A car battery is used to provide constant and continuous power to some consumers when the engine is not running, such as lighting, car radio, brake lights, anti-theft alarm, as well as to fully power all vehicle systems when the engine is started. After starting the engine, the battery is recharged from the generator, and then it works in a buffer with the generator, smoothing out voltage drops when connecting powerful consumers. The generator power of a modern middle-class passenger car ranges from about 900-1300 watts.
Older cars used DC generators that were larger and heavier than three-phase generators; To maintain a constant voltage, a relay regulator was used, consisting of three devices - a voltage regulator, a current limiter and a reverse current relay.
In a number of cases, on special-purpose vehicles, as well as on armored vehicles, an additional generator driven by a separate internal combustion engine (the so-called auxiliary power unit) is installed, which makes it possible to supply consumers with electricity regardless of the operation of the main engine.
These include: switches and switches, relays, fuses, connector blocks, distribution and switching boxes, as well as power units.
Description of "brains"
The VAZ 2114 ECU is an on-board computer of the vehicle, designed to control the main systems of the car. The parameters of the control module affect both the functionality of certain regulators and the operation of the engine as a whole.
That is, the importance of this system cannot be denied
Controller Location
In VAZ 2114 and VAZ 2115 cars, the control module is installed under the center console of the car, in particular, in the middle, behind the panel with the radio. To get to the controller, you need to unscrew the latches on the side frame of the console. As for the connection, in Samar modifications with a one and a half liter engine, the mass of the ECU is taken from the power unit housing, from the fastening of the plugs located to the right of the cylinder head.
Location of the ECU in the Chetyrka
In cars equipped with 1.6- and 1.5-liter engines with a new type of ECU, the mass is taken from the welded stud. The pin itself is fixed on the metal body of the control panel near the floor tunnel, not far from the ashtray. During production, VAZ engineers, as a rule, do not securely fix this pin, so over time it can become loose, which will lead to the inoperability of some devices.
Design and principle of operation
The control unit of the electronic system operates in accordance with the indicators received from the sensors:
- speed;
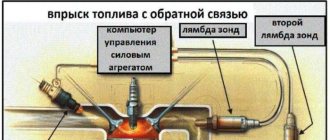
- detonation;
- lambda probe;
- fuel injection phases;
- crankshaft position;
- throttle position;
- air flow meter;
- antifreeze temperature.
In accordance with the data received from these controllers, the control module controls the following systems:
- ignition;
- adsorber;
- injectors, as well as a fuel pump;
- ventilation and heating system;
- programs for diagnosing vehicle performance;
- idle speed regulator (video author - Evgeniy Vekhter).
As for the device, the control module structurally consists of the following components:
- RAM or random access memory. This module contains basic data about recently identified errors detected by the electronic system in the operation of various components. When the driver turns off the ignition, the RAM unit is updated, causing this data to disappear.
- PROM is the main element of the system; it contains the firmware of the control module. It should be noted that this memory block contains all the necessary data on the calibration of the “four” systems along with the general engine control algorithm. Unlike RAM, EPROM is a permanent memory, so the data stored in it is retained even after the ignition is turned off. If necessary, this module can be reconfigured, that is, reprogrammed, which can lead to improved power as well as vehicle dynamics.
- ERPZU - the primary function of this module is to protect the car. The EEPROM memory contains information from the anti-theft installation - passwords, as well as encoding of the main parameters. Starting the engine will only be possible if the EEPROM successfully checks with the data contained in the immobilizer memory.
Typical malfunctions: their symptoms and causes
What are the signs that indicate a faulty ECU:
- there are no control signals coming from actuators (IAC, flow meter, various sensors, etc.);
- there is no signal for interaction with the ignition system, fuel pump, injectors and other elements;
- when connecting a diagnostic tester, there will also be no connection with the electronic system;
- Burnt contacts and mechanical damage to the device may also be a sign.
What reasons contribute to the failure of the control device:
- electrical circuit shorted or broken;
- improper electrical repairs, during which errors were made, in particular, we are talking about installing or repairing an anti-theft system;
- lighting a dead battery from a car with the engine running;
- a breakdown of the unit can be caused by incorrect connection of the battery terminals - plus instead of minus and vice versa;
- disconnecting the battery contacts when the engine is running;
- moisture on the electronic system module board;
- mechanical damage to the device as a result of an accident (the author of the video about repairing the control module in a garage is the Auto Practice channel).