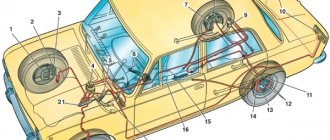
The braking system (TS) of any vehicle is designed to control the speed of movement, stop and hold it stationary for the required period of time.
It is one of the most important vehicle control systems, since road safety functionally depends on the degree of serviceability and efficiency of the braking system.
Braking system of modern cars
The general braking scheme on modern cars suggests the presence of three main types:
- working;
- spare;
- parking
The working vehicle performs the functions of reducing the speed of the vehicle or stopping it.
The spare vehicle is intended to prevent malfunction or failure of the working system.
The parking vehicle performs the functions of holding the vehicle stationary in special conditions and in parking mode. The VAZ-2107 implements a working and parking vehicle in a “pure” form.
In a modern car, braking can be performed not only by the vehicle itself, but also by the engine, electric or hydraulic transmission brake. In addition, additional systems (or devices) are often implemented that increase the productivity of braking functions:
- anti-lock braking system (the notorious ABS);
- electric brake force distribution (or EBD);
- electrical stabilization system (ESP), etc.
The described devices and systems lead to a significant increase in the cost of the vehicle, and the VAZ-2107 brake system diagram does not provide for them.
However, domestic cars have recently begun to provide similar capabilities.
Relative vehicle malfunctions
This list of faults does not apply to absolute (or categorical) faults. Their presence is associated with the convenience (or inconvenience) of driving.
Increased hydraulic pedal travel (as an option - a “soft” pedal)
The reasons for the “sinking” of the pedal are determined by the presence of air in the system; extreme wear of brake pads; failure of the main or wheel cylinders. The action plan for eliminating technical problems includes checking and repairing all components and assemblies of the system; and, if necessary, replacing failed ones and bleeding the system.
Shift towards the vehicle's trajectory when braking
The malfunction is due to either a failure of the working (wheel) cylinder or wear of the pads. Replacing them (or repairing them) will solve the problem.
Increased background noise, friction (grinding) in the brake mechanism
Deficiencies are localized mainly in the rear mechanisms and are determined by contamination of the mechanism, critical wear of the pads, breakage of spring elements, uneven wear of discs or drums. Fault repair involves washing and replacing mechanism parts.
Vibration when braking
This is a fairly common malfunction that is associated solely with critical or uneven wear of the discs or drums, and the repair will consist of replacing them.