An air lock in the engine cooling system is one of the main reasons for the engine taking a long time to warm up to operating temperature. Therefore, every driver should be interested in removing air lock from the cooling system of his car.
How to properly remove an air lock from the cooling system?
According to the law of physics, air accumulates in the highest place. In a car, the highest link in the coolant chain is the throttle body. That is why the air must be removed from there. There are several ways to get rid of an air lock. Here's the first one from the bottom:
If you have a 1.6 liter engine, then the first step is to remove the plastic cover on the engine - unscrew the cover on the engine to fill the oil, and then pull out the entire cover. It is seated on rubber seals. After removing this plastic screen, screw the oil cap back on to prevent dirt from getting into the crankcase.
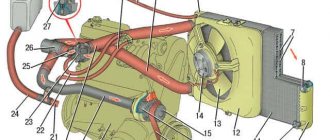
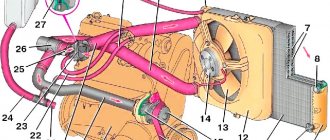
- We find the heating pipes for the throttle assembly (there are 2 of them), see the figure. Pick up any phone
- Next, unscrew the cap of the expansion tank (coolant reservoir) and cover the neck of the tank with a clean rag.
- We begin to blow into the tank with liquid. We blow until all the air comes out of the hose and antifreeze flows out.
- We quickly put the tube back on and tighten it with a clamp so that no air gets in.
(It is worth noting that depending on the tube that you removed, antifreeze may leak from both the tube and the fitting from which the tube was removed)
The second method of removing air from the cooling system is less perverted. There is no need to blow anything here:
- Warm up the engine to operating temperature
- Warm up, turn off the engine
- The expansion tank cap does NOT need to be unscrewed.
- As in the first method, unscrew the clamp of the coolant pipe on the throttle assembly.
- Having removed the heating pipe of the throttle assembly, release the air, and after the antifreeze begins to flow out, immediately put it back on the fitting and secure it well with a clamp.
But be careful and careful! Don't forget that the coolant temperature is approximately 90 degrees.
There is also a simpler, but less effective way to eliminate an air lock:
1) We drive up a steep hill so that the radiator cap becomes the highest point of the cooling system.
2) Unscrew the cap of the expansion tank and the radiator cap.
3) Let the car warm up to operating temperature
4) Then we accelerate several times and at the same time add coolant into the barrel.
Do this until bubbles stop appearing.
How to remove an air lock on a VAZ with electronic (e-gas)?
Since there is no throttle valve cooling system, you need to bypass this unit. Here you can also set the car up.
I hope that these three methods will help you solve the problem, and that you have found all the answers to your questions on the topic “How to get rid of an airlock?”
An air lock in a car's cooling system can cause problems in the operation of the engine, electronic sensors, thermostat and other mechanisms. Next, we’ll figure out how to solve the problem yourself.
FEATURES OF ENGINE COOLING VAZ 2114
This car, like the VAZ 2113 and VAZ 2115, uses a VAZ closed liquid cooling system, the coolant in which is antifreeze or antifreeze. The coolant circulates through special channels in a running engine. Its circulation is ensured by a pump, which is driven by the engine crankshaft using a drive belt.
It regulates the flow of coolant, its direction, by a device called a thermostat. It is designed in such a way that before the coolant warms up to operating temperature, it circulates in a small circle, bypassing the radiator. When the liquid reaches a temperature of 87 0 C, it opens and the liquid flow is directed to the radiator for cooling.
The radiator is blown by a flow of oncoming air, and when there is not enough air, an electric fan turns on. For these purposes, a sensor is installed in the radiator, which produces a signal to turn it on. Also, hot liquid flows through the heater radiator and heats the interior of the car in cold weather. Excess antifreeze from thermal expansion is collected in an additional tank, which is called an expansion tank.
You may also be interested
Why does the antifreeze level in the expansion tank rise?
To ensure that the engine temperature does not become critical and the car does not overheat, the cooling system needs to work. Coolant is used for this. Therefore, its level in the expansion tank is one of the most important parameters that allows you to calculate a breakdown in time.
Why antifreeze curdled: reasons and what to do
In some cases, a motorist may find foamed and heterogeneous rust-colored something under the cover. In this case, experienced drivers state: “The antifreeze has curdled.” Why does this happen and how to deal with it? This is exactly what we will discuss with experts in an article on our website.
PRESENCE OF AIR IN THE SYSTEM
Air in the engine cooling system is an unacceptable phenomenon. Heat exchange processes in the motor are disrupted, which can cause it to overheat, thereby creating the preconditions for failure. In cold weather, there will be no heating of the car interior or body glazing. Sensors installed in injection engines begin to provide distorted information to the electronic control unit, which disrupts the engine’s operating cycle.
WHY DO AIR LOCKES OCCUR?
In order for an air lock to occur in the cooling system, one of several possible reasons for its occurrence is sufficient. These may be such violations in the operation of the system:
How to bleed air from the VAZ 2114 engine cooling system
Malfunctions that occur in the ODS can significantly ruin the life of the driver. For example, when an air lock forms in the cooling system, well-heated air stops flowing into the cabin due to the fact that antifreeze does not flow into the heater stove. The engine cools worse and there is no normal heat exchange in the system. As a result, the entire internal combustion engine or individual units overheat, which reduces the life of the power unit. The operation of some sensors is distorted, which also negatively affects the overall condition of the car.
Why do air pockets form in the cooling system? There are several reasons:
- There is suction in the system due to loose pipes. This happens more intensely in winter. At low temperatures, plastic shrinks, and if the clamps are not tightened in time, then a plug in the cooling system is guaranteed;
- the valve on the expansion tank cap may be faulty;
- the seal of the pump is broken;
- cracks or leaks have appeared on cooling or heating radiators;
- A cylinder head gasket failure was discovered.
More serious reasons are possible, such as:
- clogging of radiators or pipes, as well as some mechanical damage to them;
- deformation or breakage of the pump impeller;
- partial thermostat failure;
Before removing the air lock from the cooling system of the VAZ 2114, it is necessary to thoroughly diagnose it for blockages, breakdowns and leaks. This must be done so that the work done later is not in vain. In addition, it is necessary to check the functionality of the thermostat. If it turns out to be completely or partially faulty, you can clean the system of air as much as you like, it will not work better.
Before starting work, you need to prepare antifreeze for adding to the system, if necessary. Also, rags and, preferably, two pairs of gloves - cotton, work and household, rubber. You have to work with an aggressive liquid, especially one heated to 80-90 degrees.
There are several options for removing air from the engine cooling system.
- An air lock forms at the top of the system. On a VAZ 2114 this is a throttle assembly. To get to it, you need to remove the cover covering the engine from above. After this, one of the two cooling system tubes suitable for the remote control is disconnected. The clamp must be left on it so that later you can put it back on and seal it as quickly as possible. Remove the cap from the expansion tank and, covering the neck with a thick rag, insert the pump and create pressure in the tank to remove the air lock in the cooling system. After antifreeze flows from the disconnected tube, you need to quickly put it in place and secure it.
Some experts recommend blowing into the neck of the tank to squeeze out antifreeze, but this cannot be done for two reasons. The main thing is that antifreeze or antifreeze is a toxic poison for the human body, and secondly, in order to blow effectively, you need to strain, and such “exercises” are of little use to anyone and can cause spasms.
- Another option for removing air from the VAZ 2114 cooling system is as follows.
Principles of designing cooling systems
A decrease in the efficiency of the cooling system leads to an increase in the temperature of the pistons and a decrease in the gaps between the piston and the cylinder. Thermal gaps are reduced to zero. The piston touches the cylinder walls, scoring occurs, overheated oil loses its lubricating properties and the oil film breaks. This mode of operation can lead to engine seizure. Overheating is accompanied by uneven expansion of the cylinder head, mounting bolts, engine block, etc. Subsequent destruction of the engine is inevitable: cracks in the cylinder head, deformation of the joint planes of the head and the cylinder block itself, cracks in the valve seats, etc. — it’s unpleasant to even list all this, so it’s better not to let it come to that!
The engine and oil cooling system is designed to prevent such developments, but in order for the system to cope with its tasks, it is necessary to use high-quality coolant (coolant). Low-freezing coolants are called antifreeze - from the English word “antifreeze”. Previously, coolants were prepared based on aqueous solutions of monohydric alcohols, glycols, glycerin and inorganic salts.
Currently, preference is given to monoethylene glycol, a colorless syrupy liquid with a density of approximately 1.112 gcm2 and a boiling point of 198 g. The task of coolant is not only to cool the engine, but also not to boil over the entire operating temperature range of the engine and its components, to have high heat capacity and thermal conductivity, not to foam, not to have a harmful effect on pipes and seals, and to have lubricating and anti-corrosion properties.
In the 70s, antifreeze was produced based on an aqueous solution of monoethylene glycol with a crystallization temperature of 40 degrees. It did not require dilution with water when added to the cooling system. This drug was called TOSOL - after the name of the laboratory “Technology of Organic Synthesis”. Because the name is not patented, then TOSOL is a ready-to-use product, and “antifreeze” is a concentrated solution (although TOSOL is also antifreeze).
Ready-made antifreezes are colored for safety and catchy colors are chosen: blue, green, red. During operation, antifreeze loses its beneficial properties - its anti-corrosion properties decrease, and the tendency to foam increases. The service life of domestic coolants is from 2 to 5 years, imported 5-7 years.
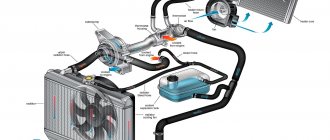
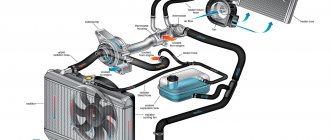
The figure below shows a diagram of the car's cooling system. There is nothing special or complicated in the cooling system and yet...
Rice. 1 - engine, 2 - radiator, 3 - heater, 4 - thermostat, 5 - expansion tank, 6 - radiator cap, 7 - upper pipe, 8 - lower pipe, 9 - radiator fan, 10 - fan switch sensor, 11 - sensor temperature, 12 - pump.
When the engine starts, the water pump begins to rotate. The pump drive may have its own pulley driven by an accessory belt or driven by the rotation of a timing belt. The cooling system contains an impeller, which rotates and drives the coolant. To quickly warm up the engine, the system is “shorted”, i.e. The thermostat is closed and does not allow fluid to enter the radiator. As the temperature of the coolant rises, the thermostat opens, transferring the system to another state when the coolant passes along a long path - through the radiator of the cooling system (the short path is blocked by the thermostat). Thermostats have different opening characteristics. Typically the opening temperature is marked on the edge. It’s probably not worth explaining the design of the radiator. A fan switch sensor is installed at the bottom of the radiator. If the coolant temperature reaches a certain value, the sensor will close, and because If it is electrically connected to the break in the power supply circuit of the electric fan, then when it is shorted, the cooling system fan should turn on. As the coolant cools, the fan turns off and the thermostat closes the long path to a short one. It's simple, but not very...
We recommend: How to choose summer tires? Tips for choosing summer tires
This scheme is the basis, but life does not stand still and various manufacturers are improving cooling systems. On some cars you will not find a sensor for turning on the cooling fan, because... The fan is turned on by the engine ECU depending on the readings of the coolant temperature sensor. It is worth paying attention to the situation in which when the ignition is jammed, the cooling system fan immediately turns on. Either the temperature sensor is faulty, or its circuits are damaged, or the engine ECU itself is faulty - it “does not see” the engine temperature and, just in case, immediately turns on the fan.
On some cars, special electric valves are installed on the way to the heater, allowing or blocking the path of coolant (BMW, MERCEDES). Such valves sometimes “help” the cooling system fail.
Reasons for decreased performance
Despite the simplicity of the design, problems with the VAZ-2114 stove often arise. They are mainly associated with a drop in the performance of the heating system - the stove heats the air poorly, blows cold or slightly warm air. In this case, the reasons for poor operation of the stove can be both general (warming up is weak at any control unit settings) and when operating in a certain mode, for example, at idle. Or, for example, cold air or slightly warm air blows only on the side windows, and in other modes the heating works normally.
Common reasons why the stove stops heating:
- the heater radiator is clogged or an air lock has formed in it;
- when switched to heating mode, the heater damper does not fit tightly to the body, which is why part of the air flow moves bypassing the radiator and enters the cabin cold;
- the tap does not open completely - this is one of the main reasons for a poorly heating stove;
- the formation of cracks at the joints of the housing and air ducts, which causes strong dispersion of the air flow.
It is not difficult to determine the cause of a general decrease in the efficiency of the heating system. To find out why the VAZ-2114 stove does not heat well, you need to remove the side decorative panels from the center console, and then warm up the engine and turn on the stove at maximum power. After this, we try the antifreeze supply pipe to the heater radiator up to the tap and behind it. The same heating temperature of the tube on both sides indicates that the tap is working properly and the problem lies in the radiator. If after the tap the pipe is less warmed up, the tap is jammed or does not open completely.